Visual impairments refer to a range of conditions that affect a person’s ability to see clearly or at all. Not everyone with a visual impairment is completely blind—some may have partial vision or difficulties with color recognition.

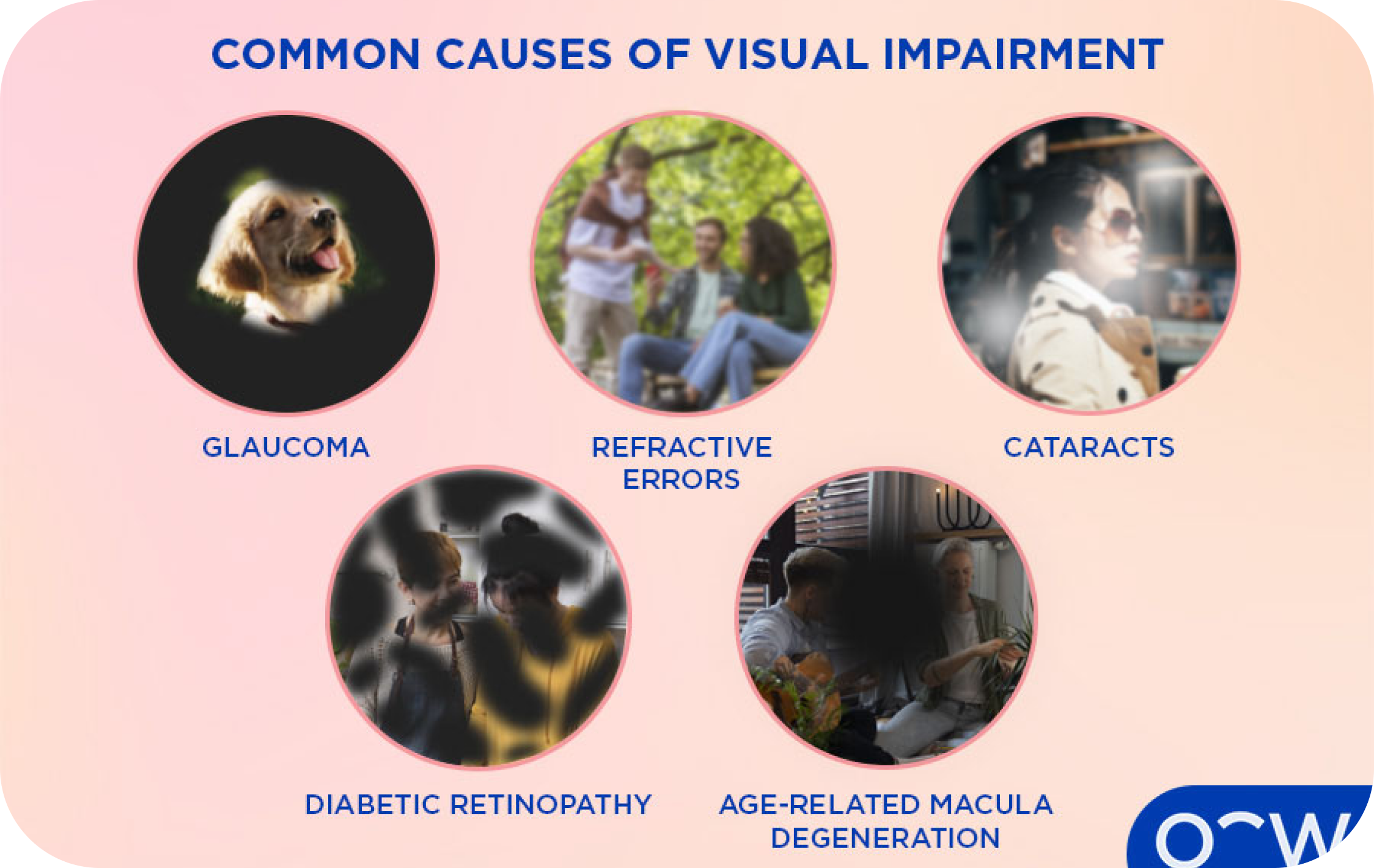
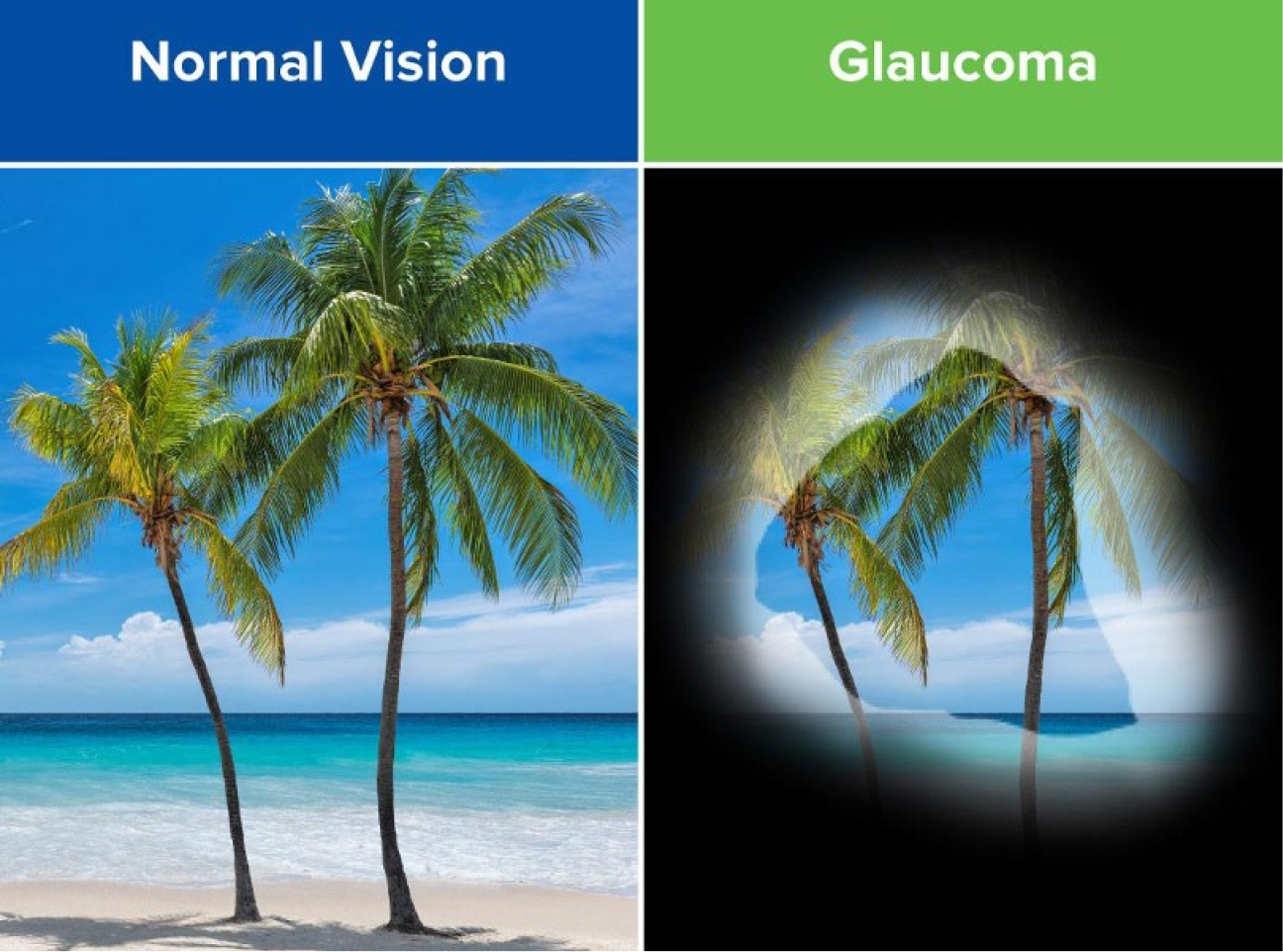
A condition causing damage to the optic nerve, often due to high eye pressure, leading to gradual vision loss.
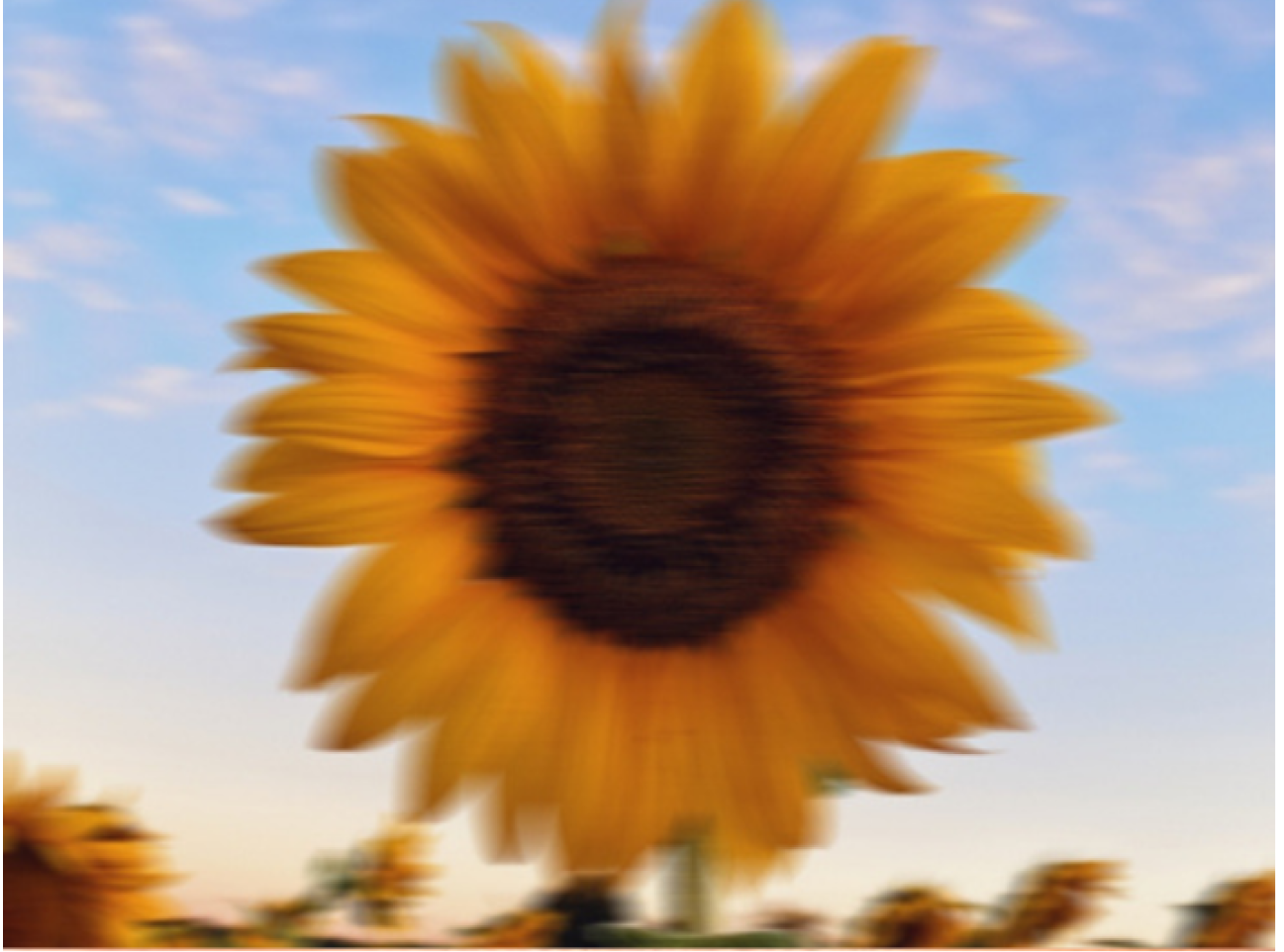

Vision problems like nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism caused by the eye's inability to properly focus light.

Clouding of the eye's natural lens, causing blurry vision and difficulty seeing clearly.

Vision impairment caused by damage to the blood vessels in the retina due to diabetes.

A condition affecting the central part of the retina, leading to loss of central vision, especially in older adults.

Difficulty distinguishing certain colors, like red and green or blue and yellow.
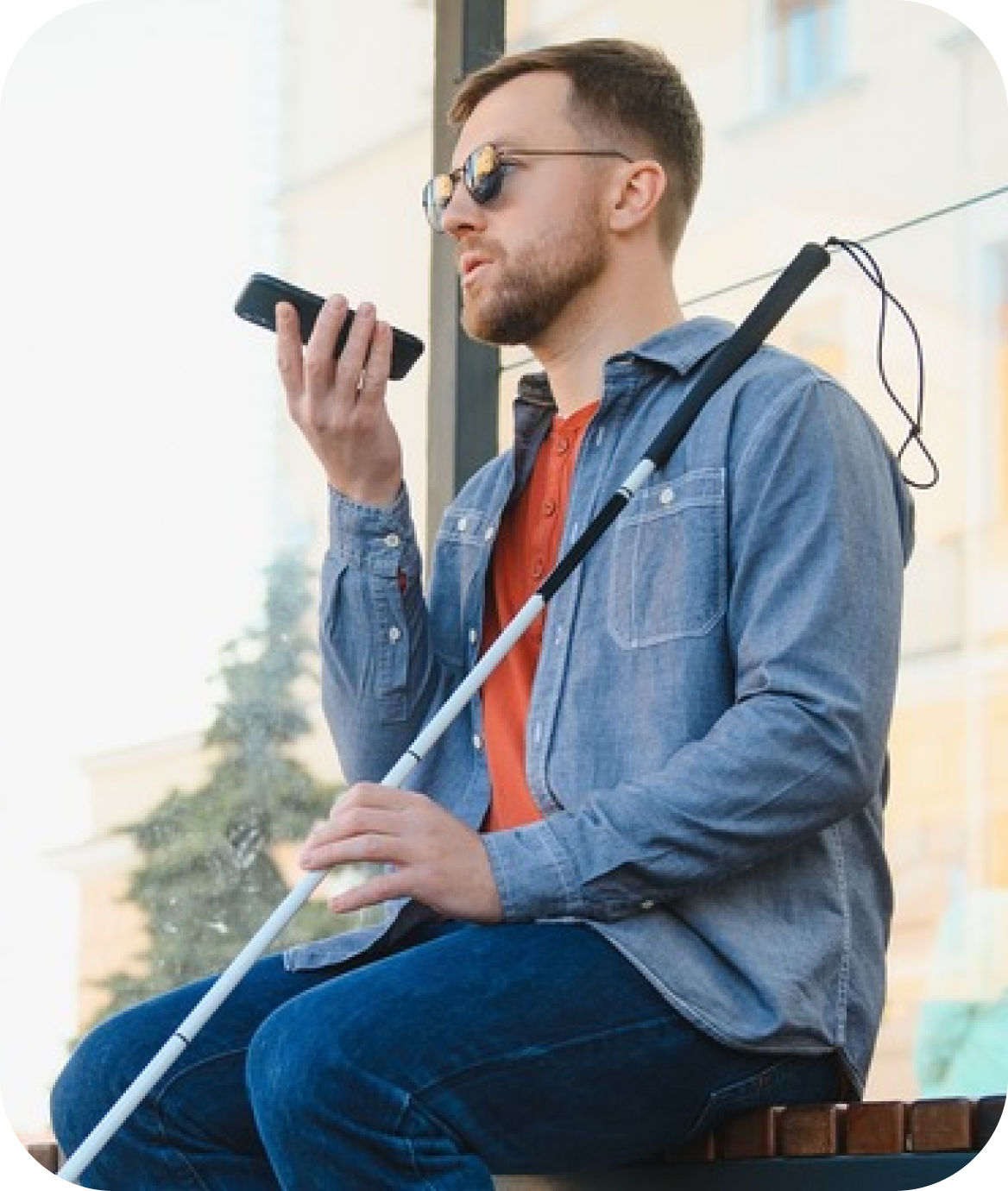

Challenge:
Individuals with visual impairments often face difficulties identifying obstacles and finding their way in unfamiliar or complex environments. This may include hazards like uneven flooring, furniture placement, and crossing streets.
Solution:
Use navigation apps with voice guidance, tactile paving for guiding pathways, and smart canes equipped with sensors to detect obstacles.
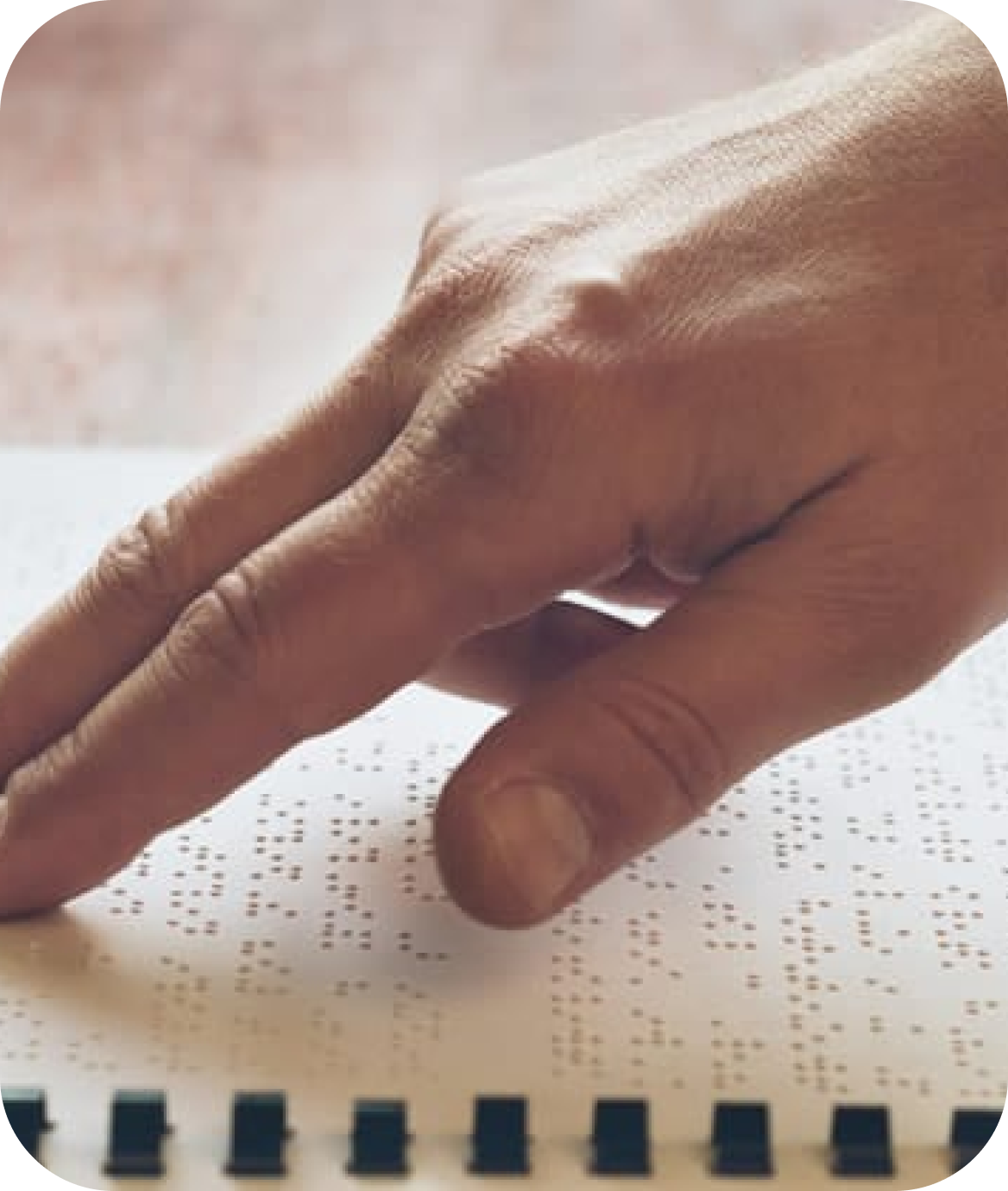

Challenge:
Small font sizes, poor contrast between text and background, and overly cluttered layouts make reading challenging. This applies to both printed materials and digital interfaces.
Solution:
Implement high-contrast modes, magnification software, and accessible design principles such as large, clear fonts.
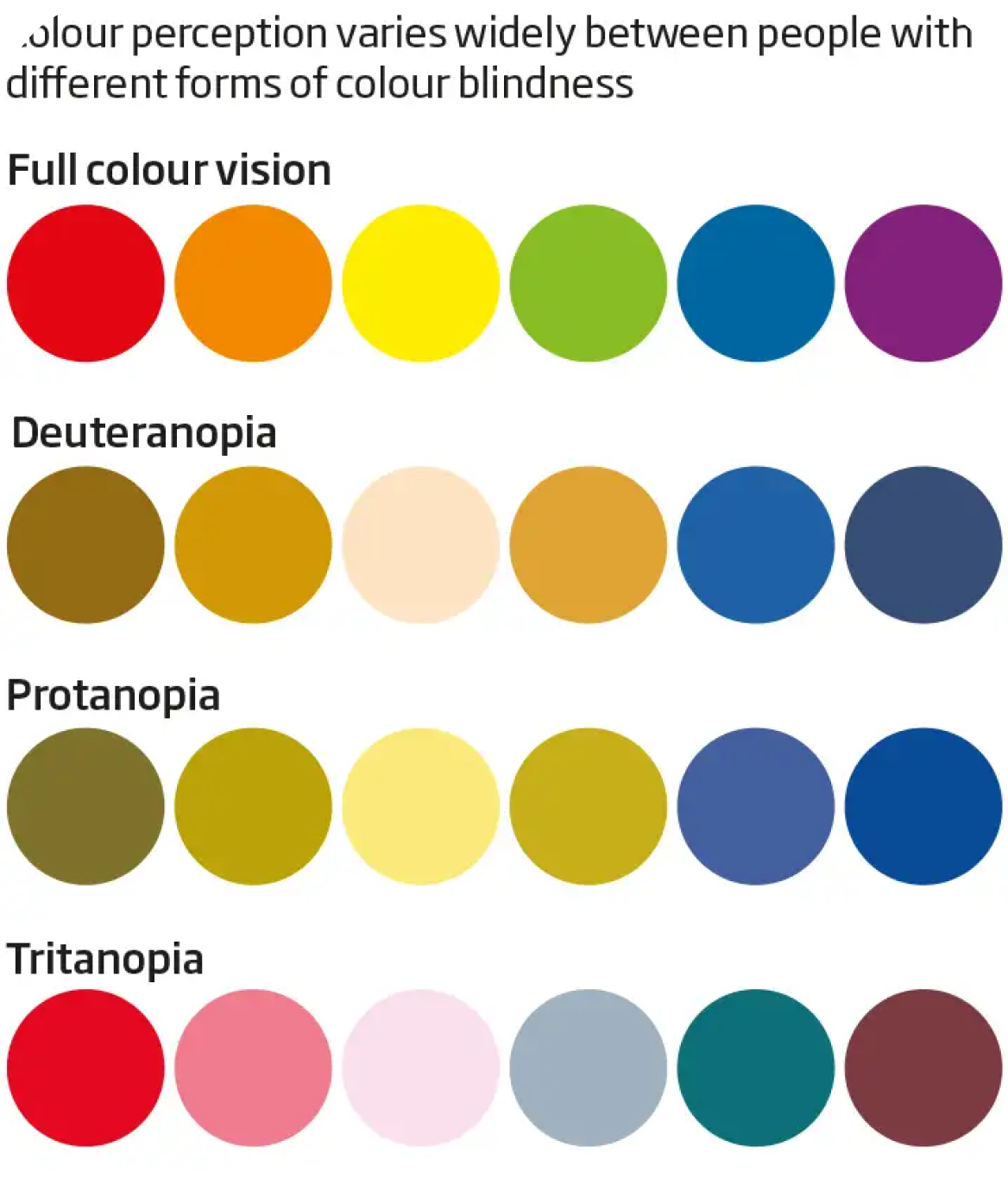
Challenge:
For those with color blindness, interpreting color-coded information such as charts, maps, or warning signals becomes difficult.
Solution:
Use textures or patterns in addition to colors, and ensure charts and maps are labeled with text descriptions.
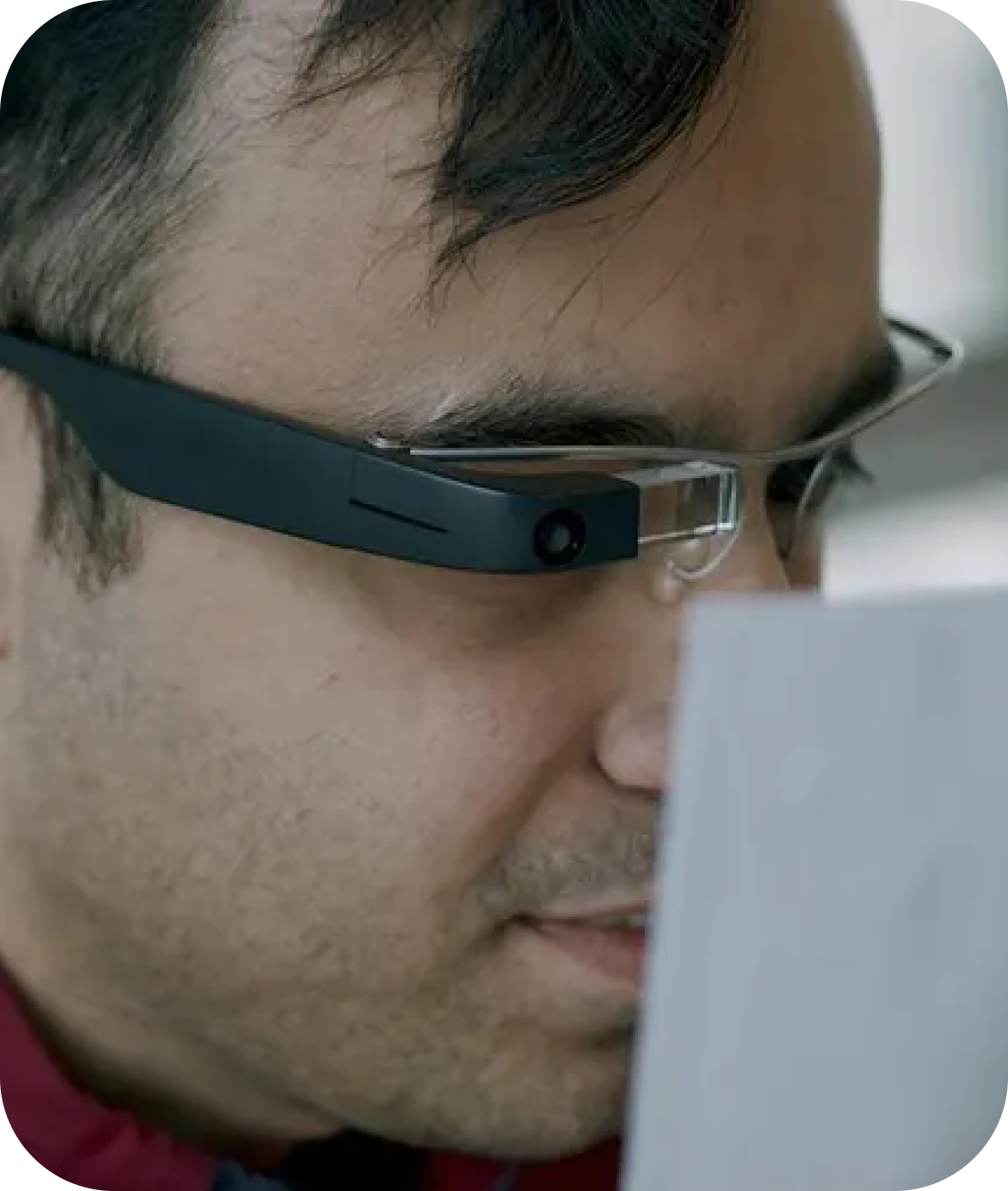

Challenge:
Visual impairments can make it challenging to identify familiar faces or recognize objects, leading to social and practical difficulties.
Solution:
Smart glasses with object and facial recognition features, and AI-driven assistive apps that provide audio descriptions.