Mobility loss refers to the partial or total inability to move or walk freely due to physical conditions that affect the muscles, bones, or nervous system. Individuals with mobility loss may experience difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or performing everyday activities. It can range from mild limitations to complete immobility and often requires adjustments in daily life to maintain independence and quality of life.
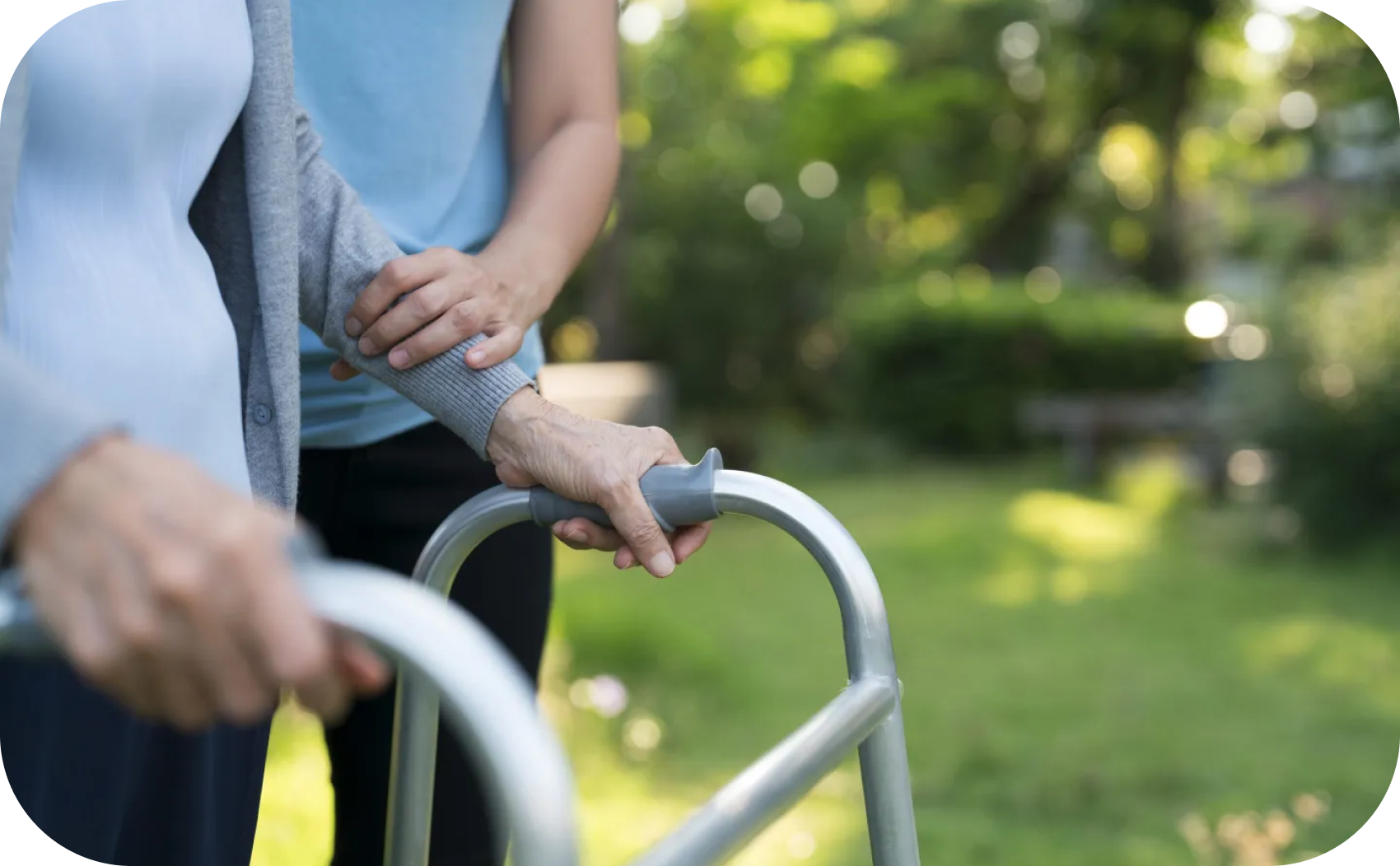
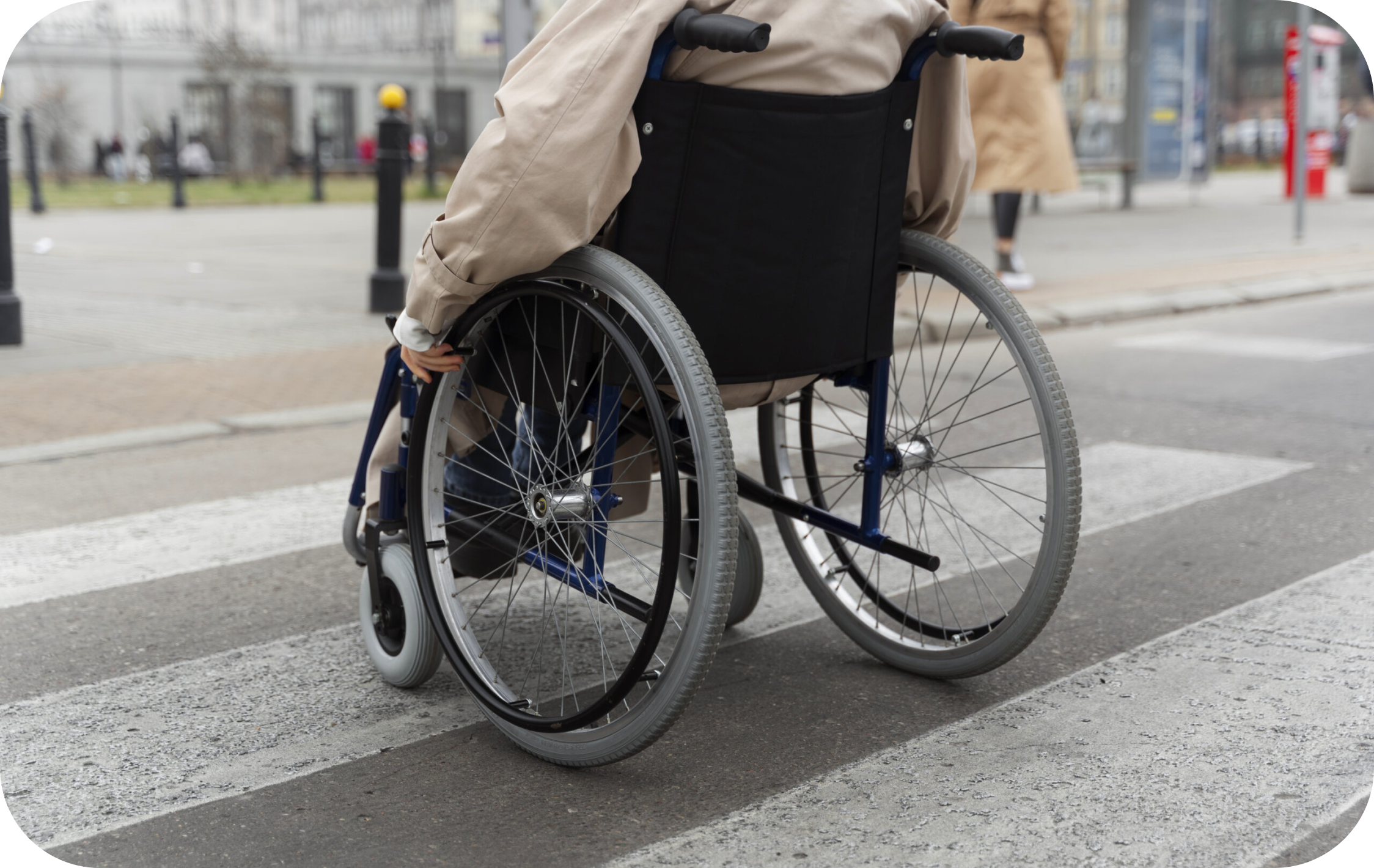


Conditions like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, or cerebral palsy can interfere with muscle control and coordination.
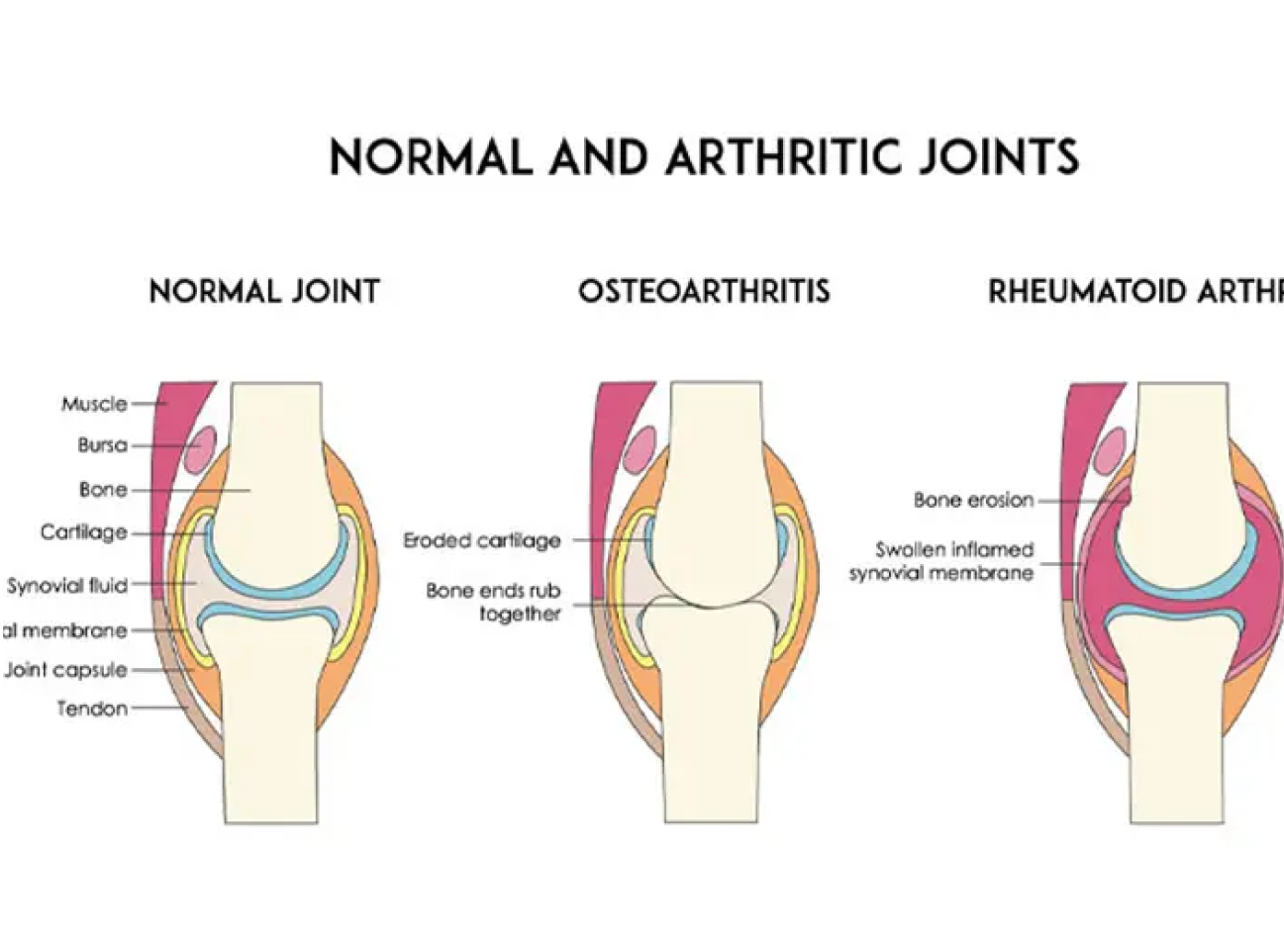
Joint inflammation, such as in osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, can cause pain and stiffness, limiting movement.

Traumatic injuries to the spinal cord, legs, or feet can lead to permanent or temporary mobility challenges.
A group of genetic diseases causing muscle weakness and loss of function over time.
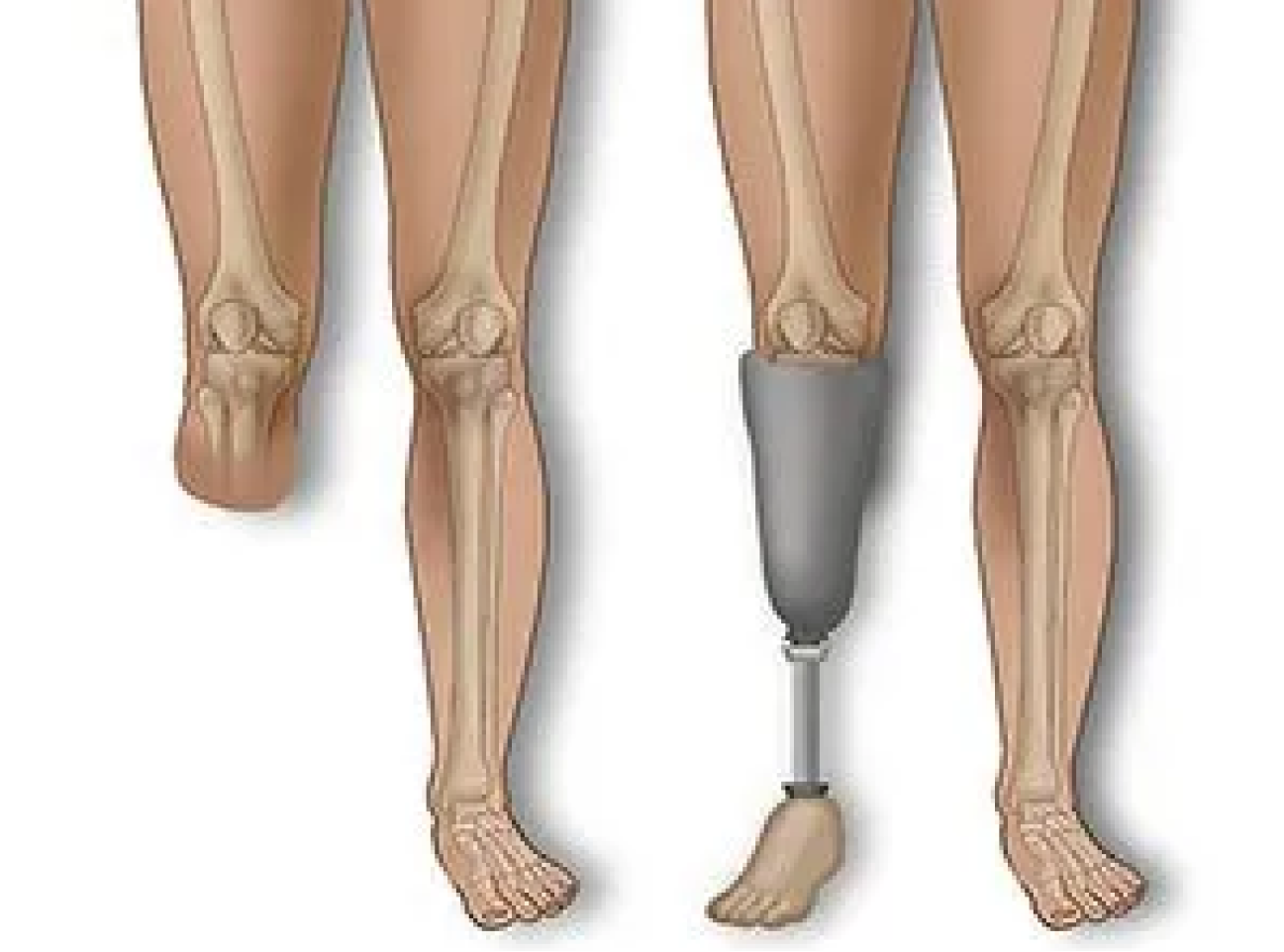
The loss of a limb, due to injury, disease, or surgery, can affect mobility and require adaptive techniques or prosthetics.
Excessive weight can strain the joints and make it more difficult to move or perform physical tasks.
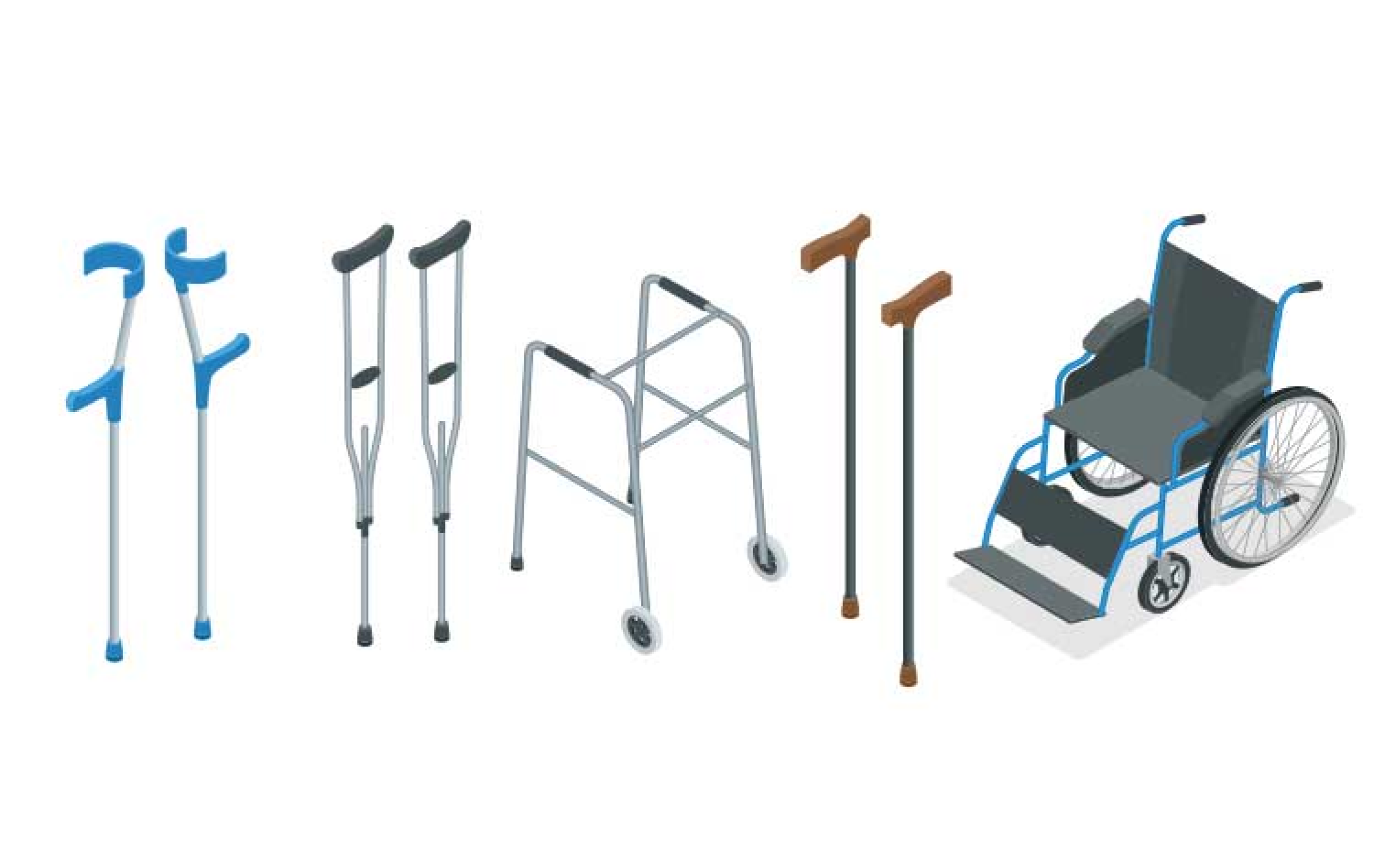

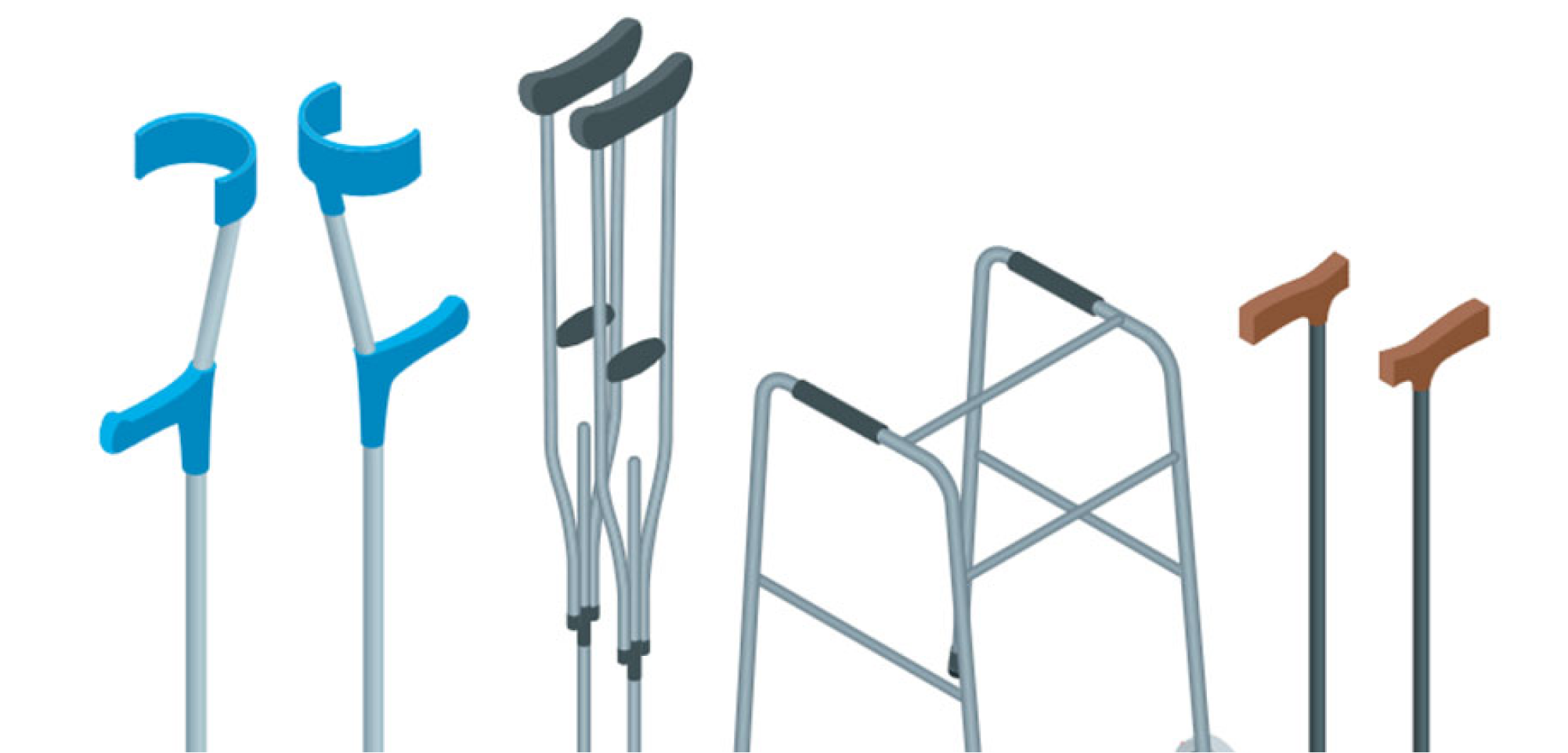
Provide balance and stability

Manual or powered options for those who cannot walk
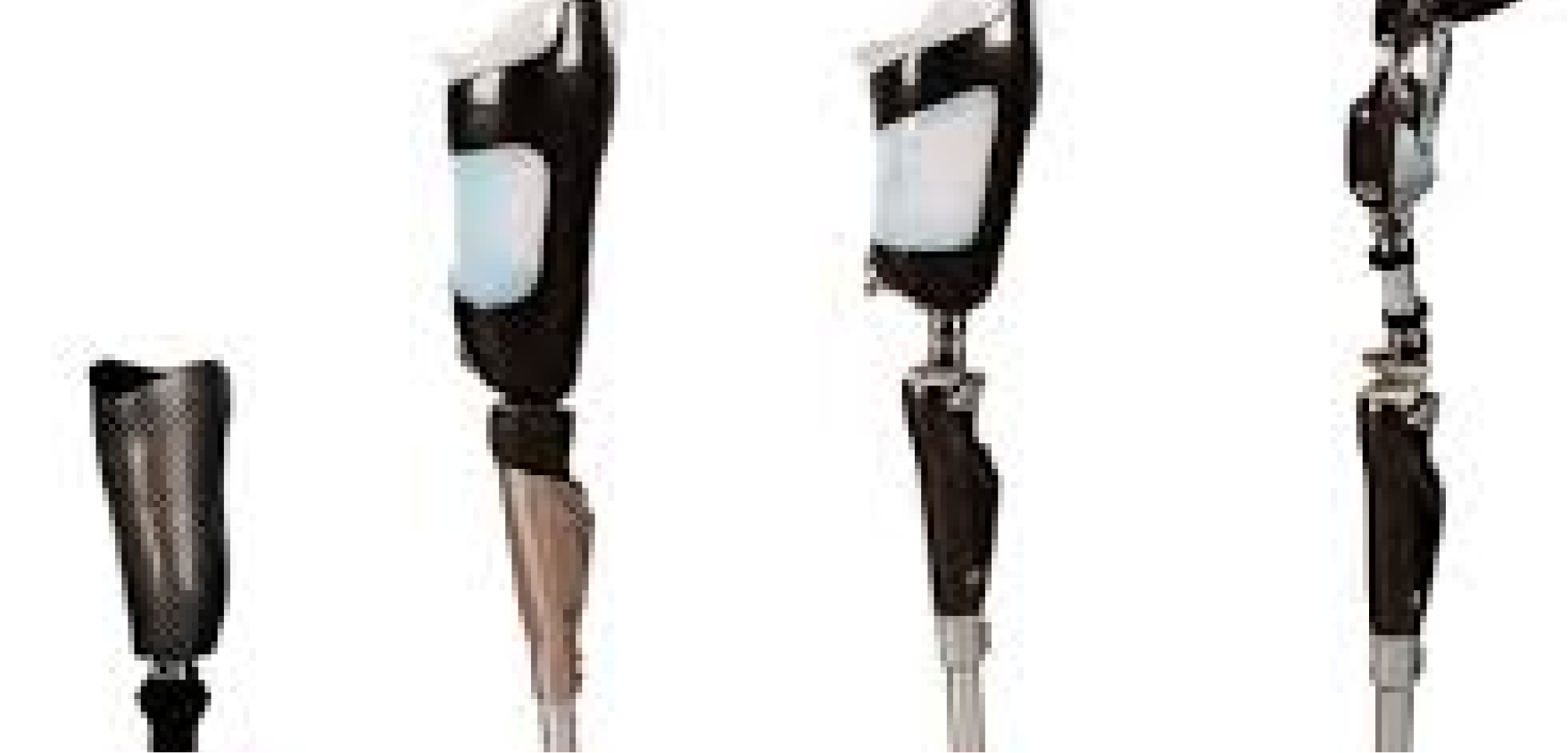

Artificial limbs for enhanced mobility

Exoskeletons that help individuals walk
Smart prosthetics controlled by neural signals
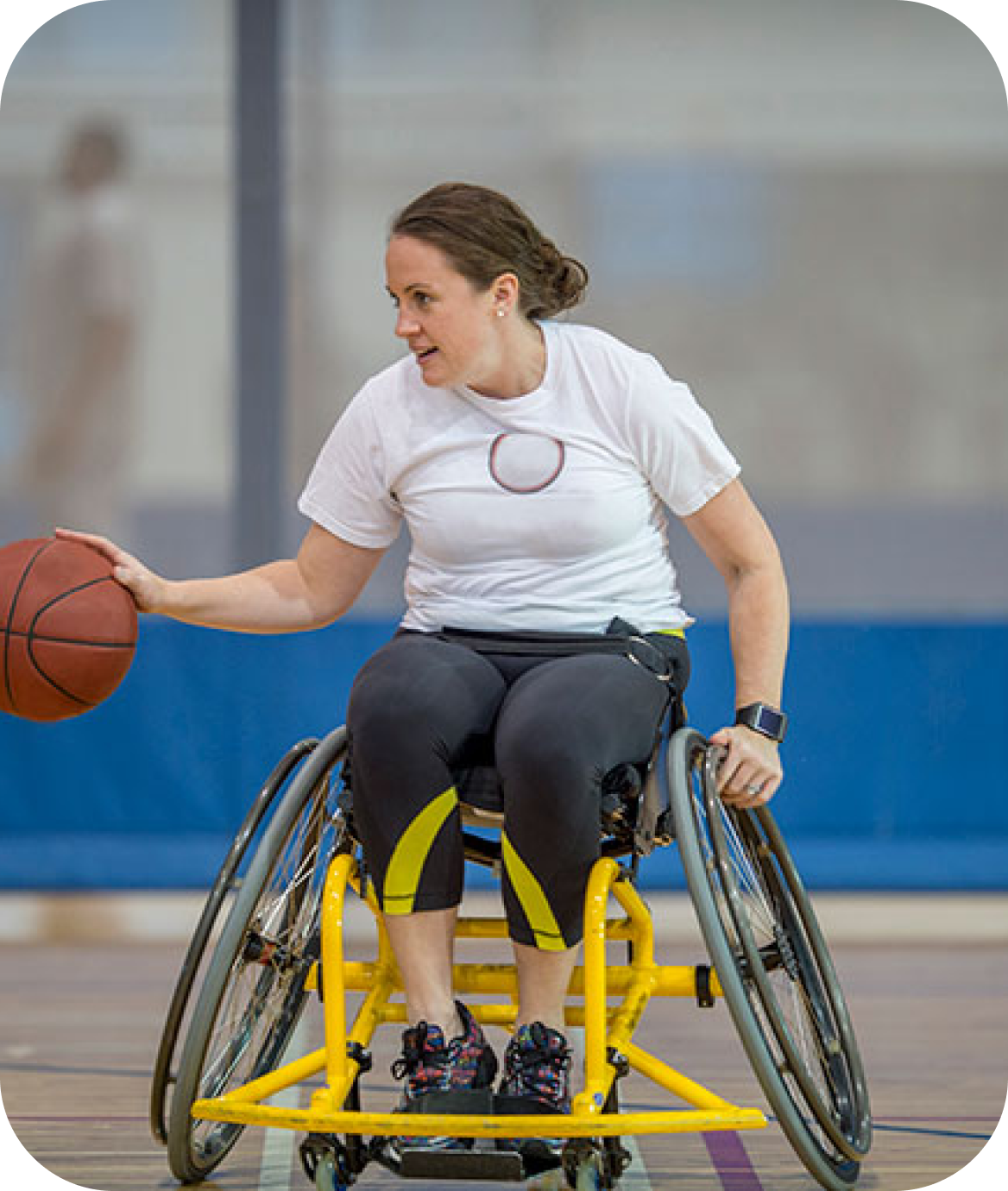

Challenge:
Solution:
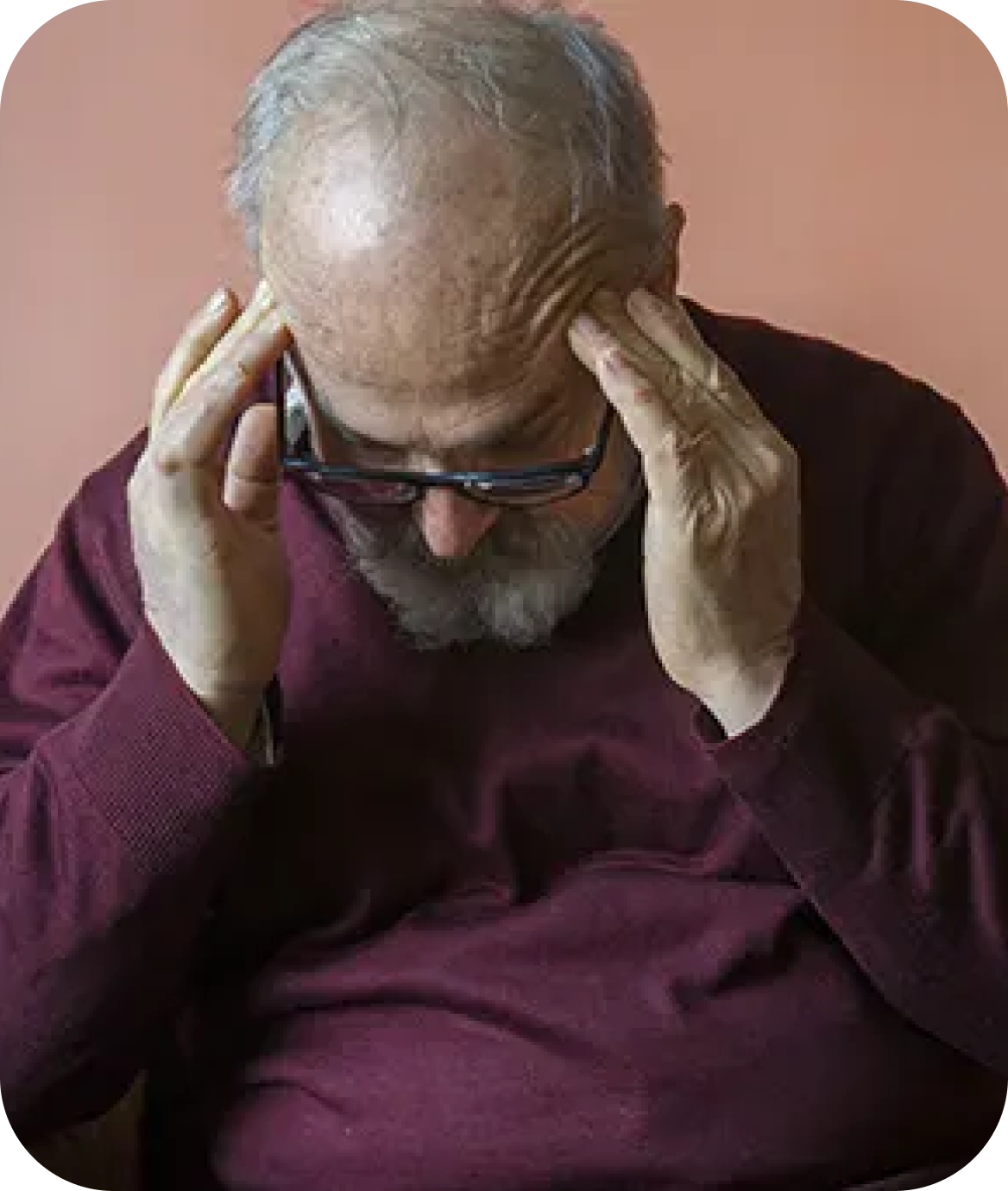

Challenge:
Solution:
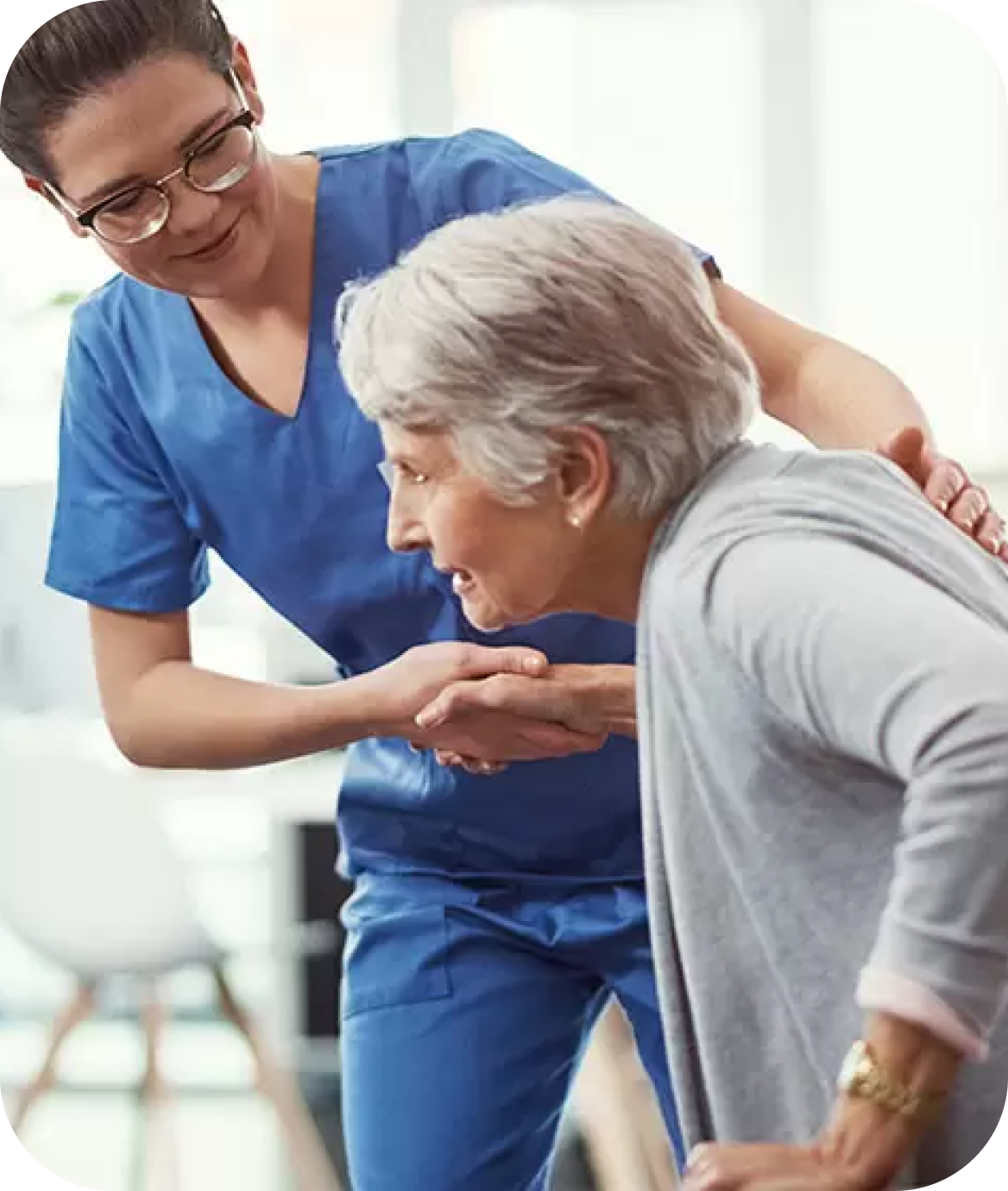

Challenge:
Solution:
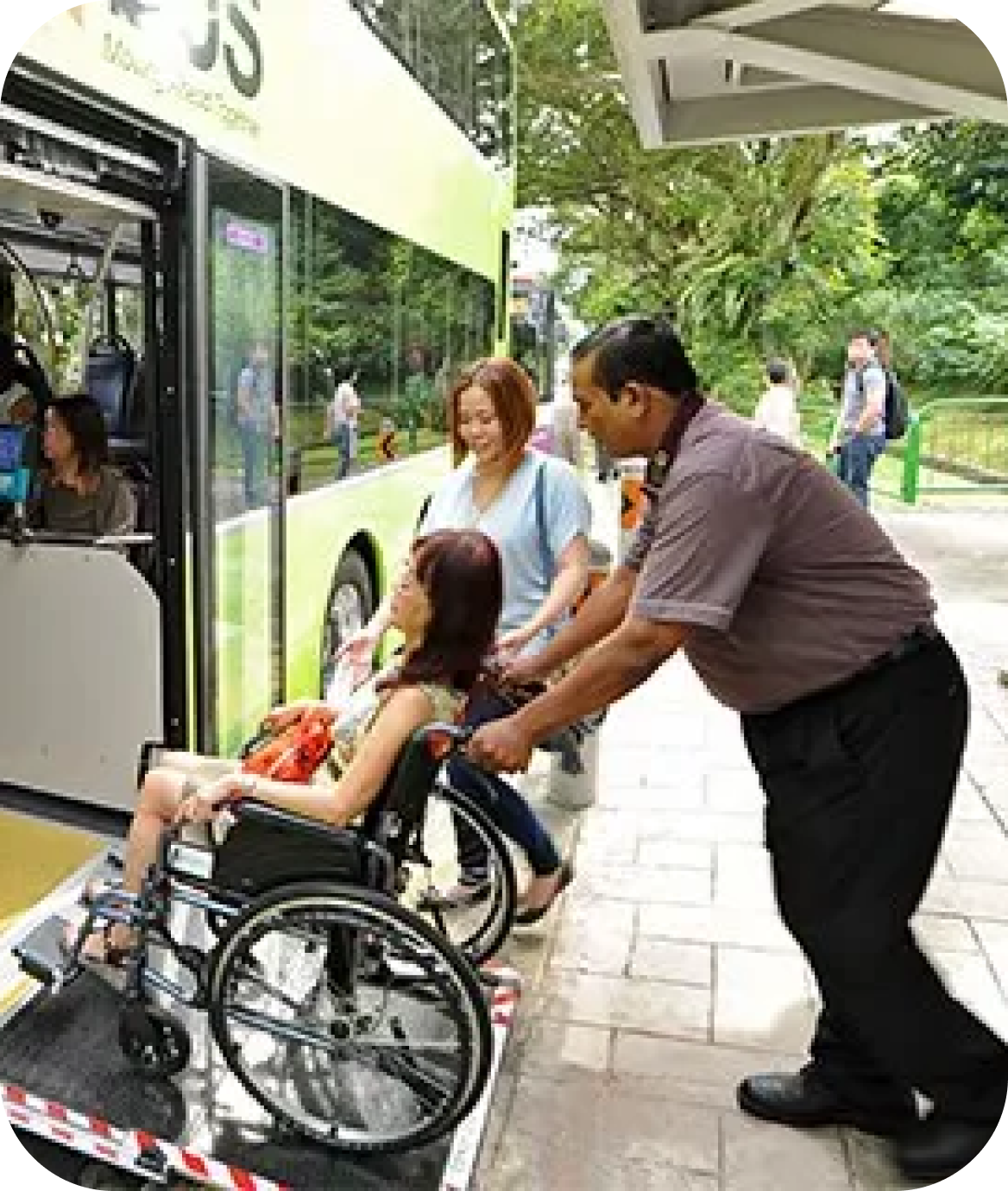

Challenge:
Solution: