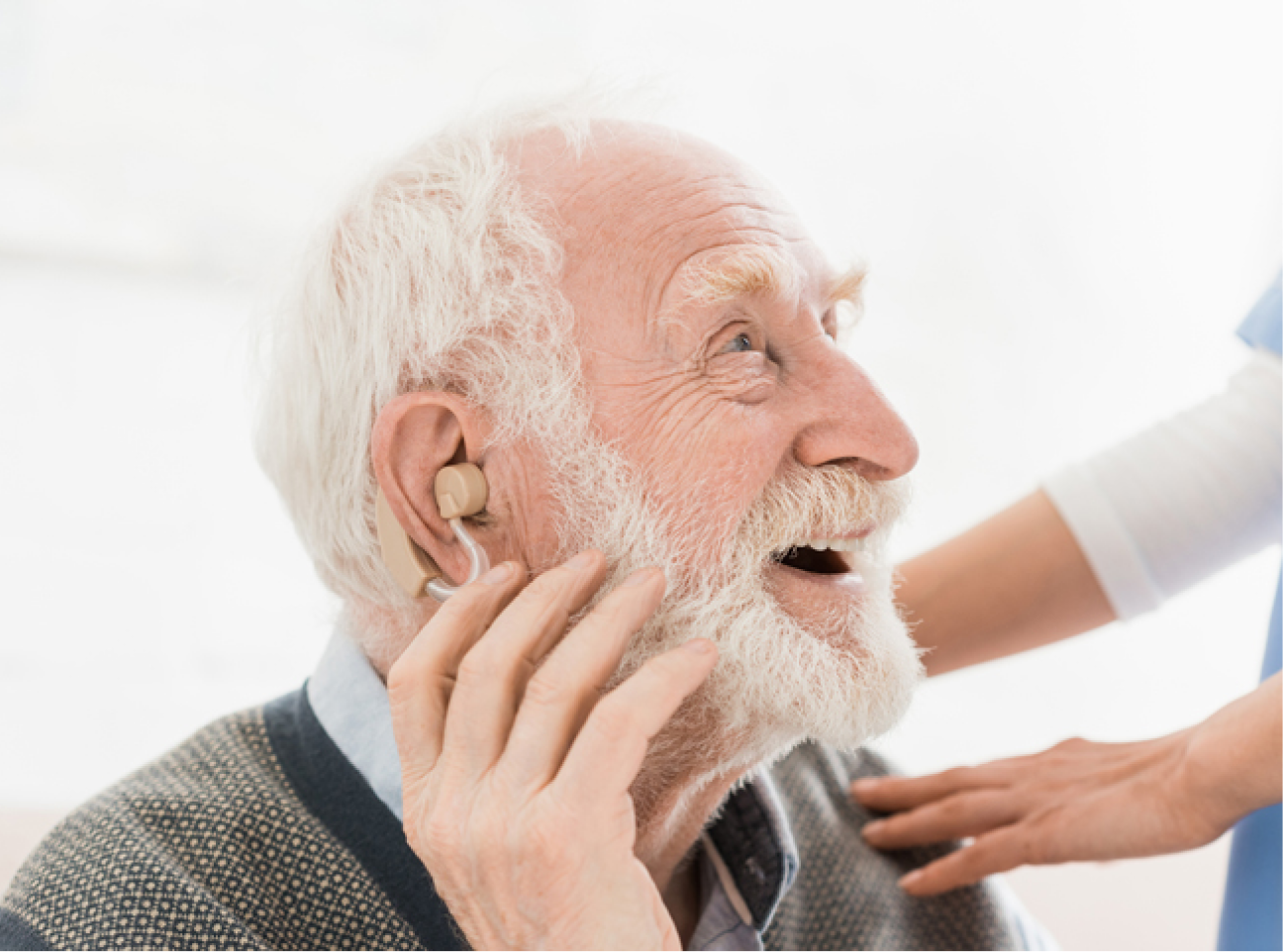
Hearing loss refers to the partial or total inability to hear sounds, affecting a person’s ability to communicate and interact with the world around them. It can occur gradually or suddenly and may be temporary or permanent. Understanding hearing loss is crucial for fostering an inclusive environment where individuals can fully participate in society, regardless of their hearing abilities.

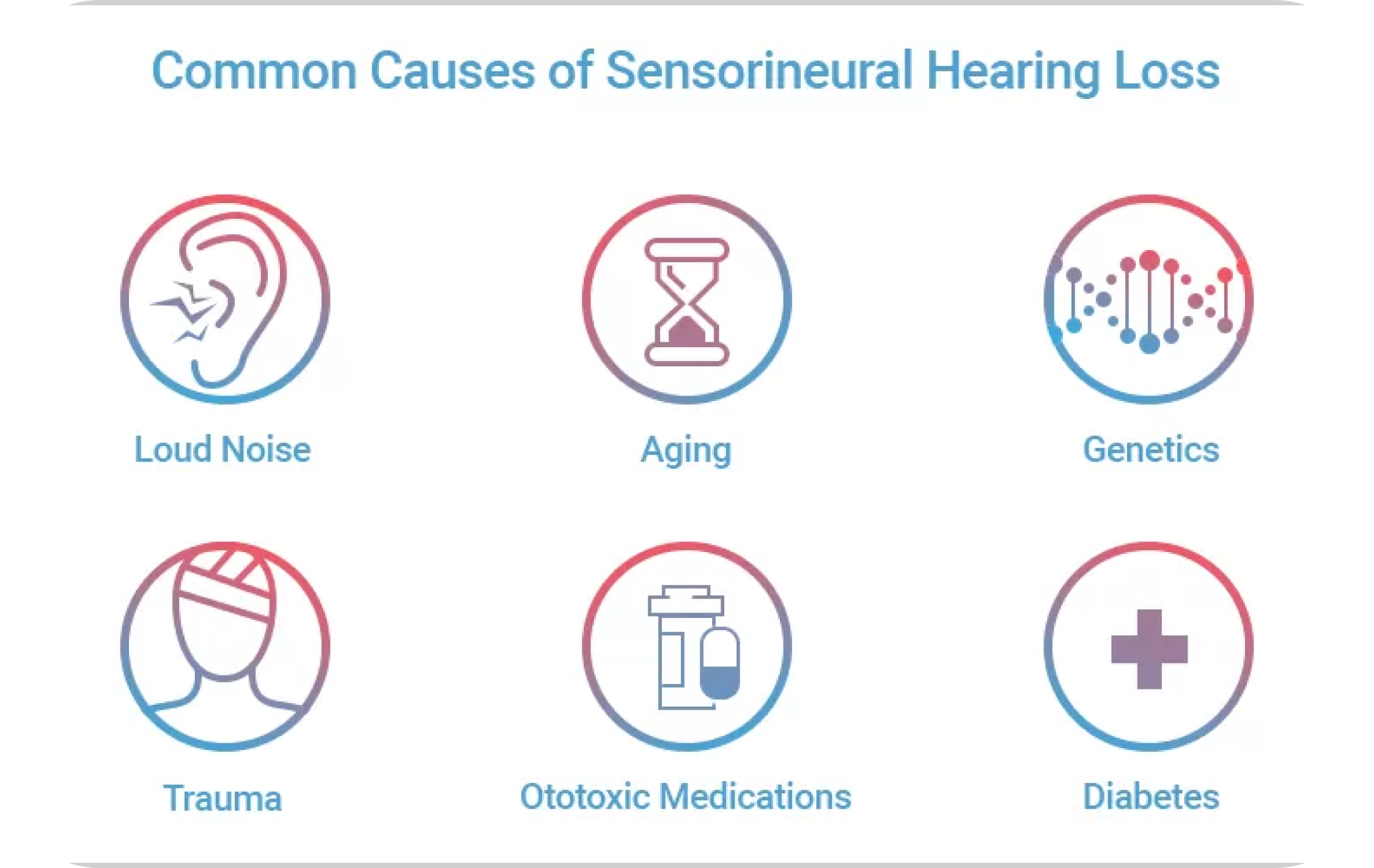

Gradual decline in hearing ability due to age-related changes in the ear.
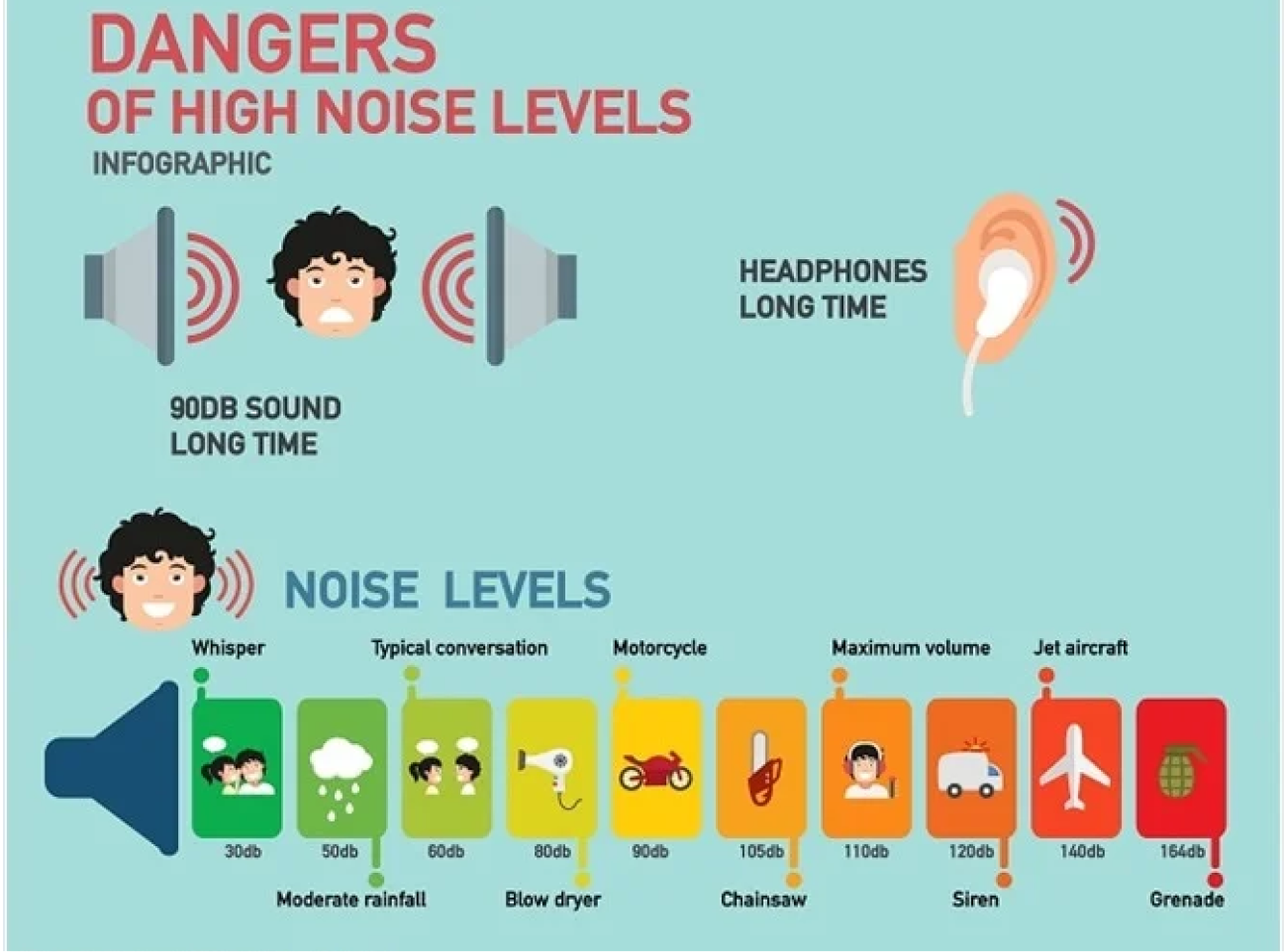
Prolonged exposure to loud sounds, such as at concerts or in noisy workplaces.
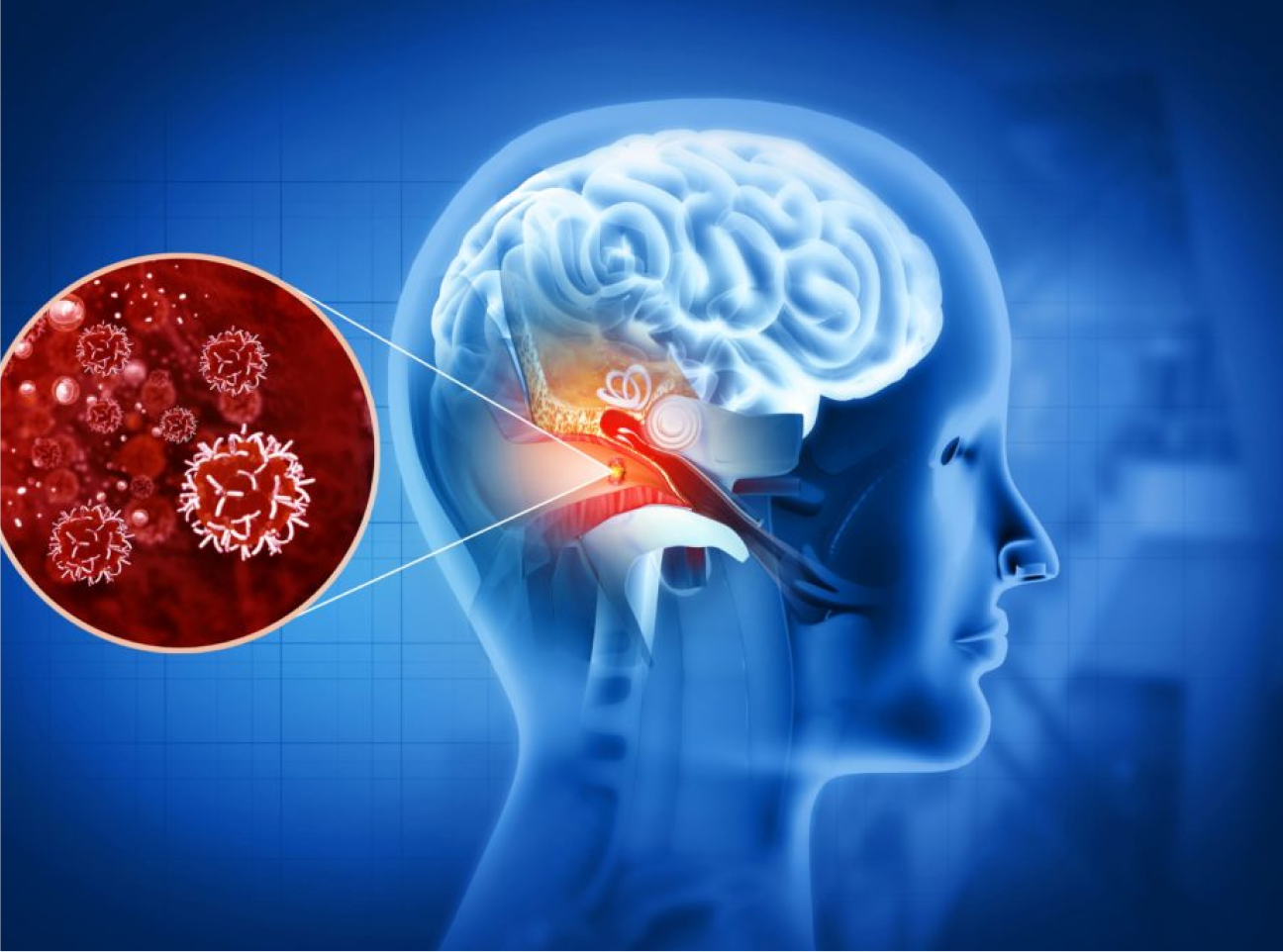
Ear infections or illnesses like meningitis can damage the hearing structures in the ear.

Hereditary conditions or congenital deafness.

Physical trauma to the ear or head can lead to hearing loss.

Certain medications, like those used for chemotherapy, can damage the hearing structures.
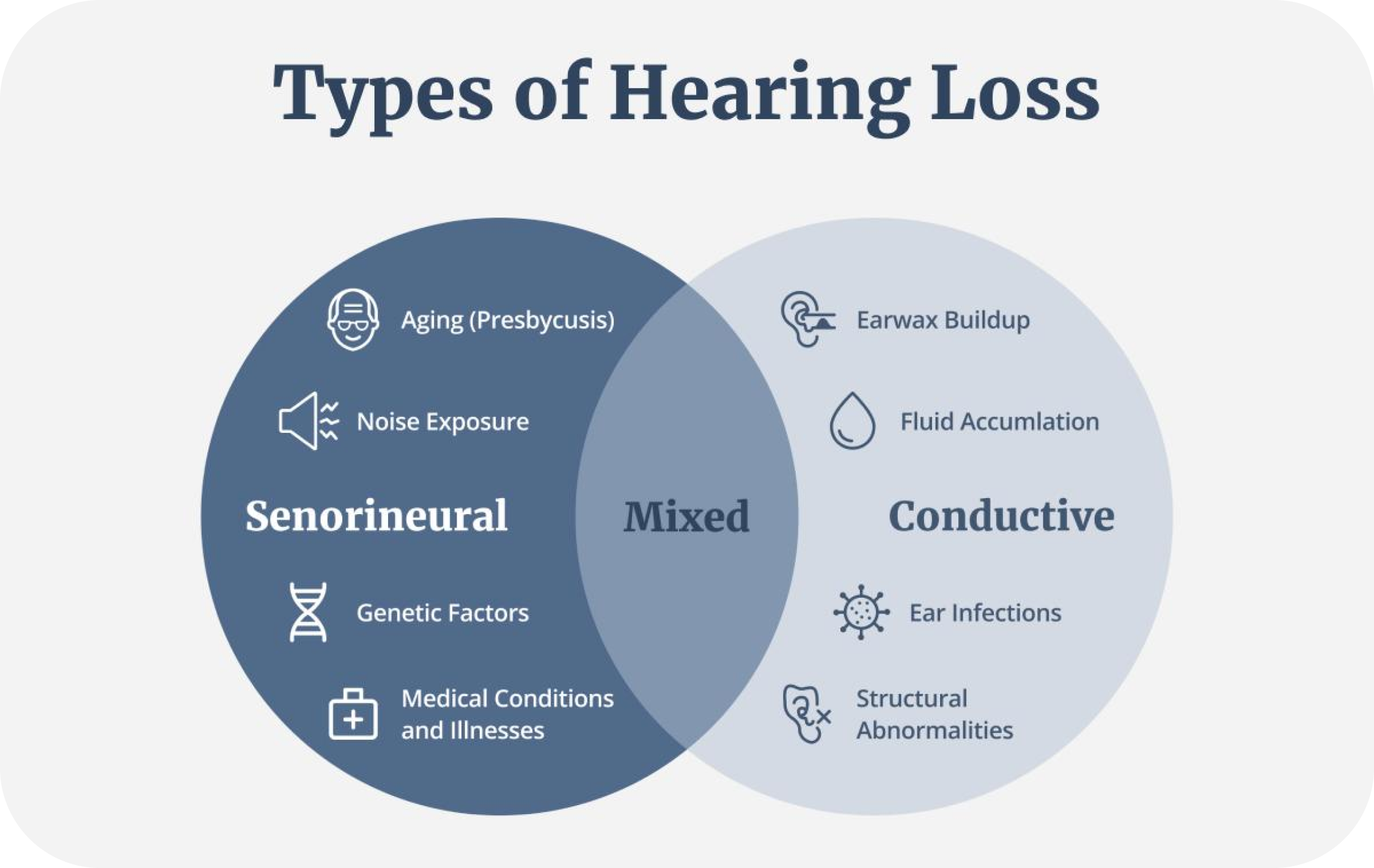
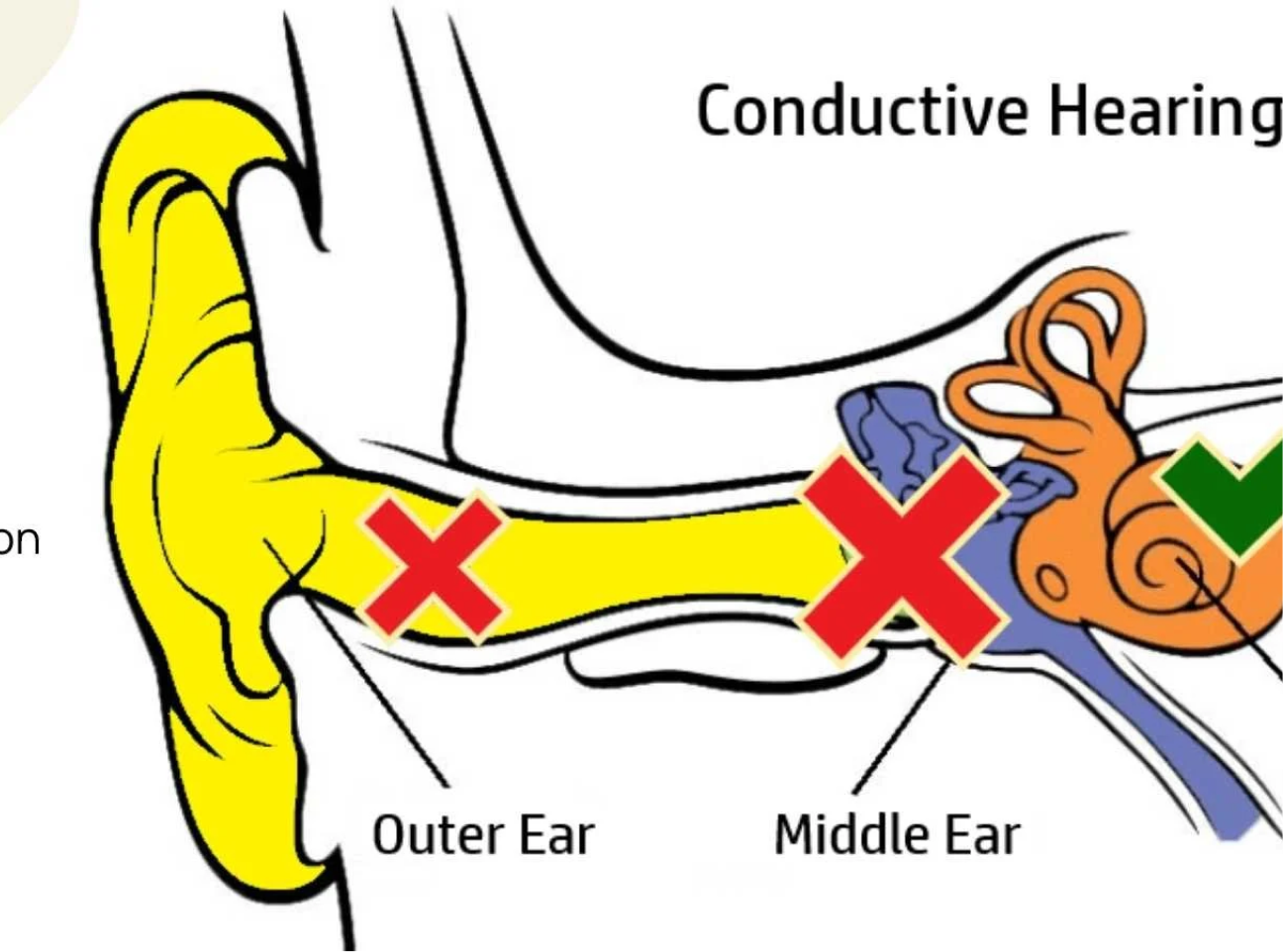
Occurs when sound waves cannot reach the inner ear due to obstructions or damage in the outer or middle ear. This may be caused by ear infections, fluid buildup, or earwax blockage.
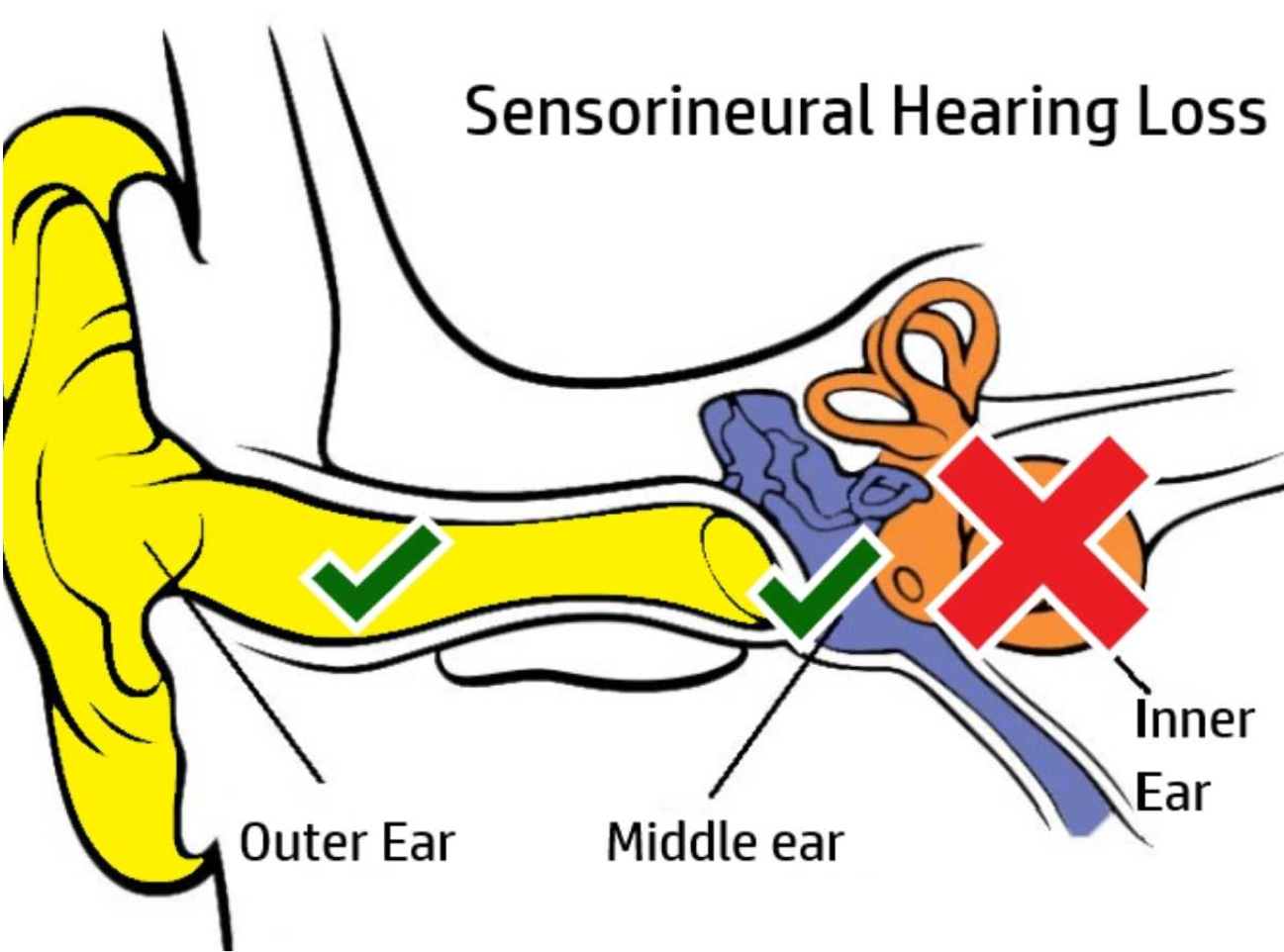
Results from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. It is usually permanent and can be caused by aging, noise exposure, or genetics.
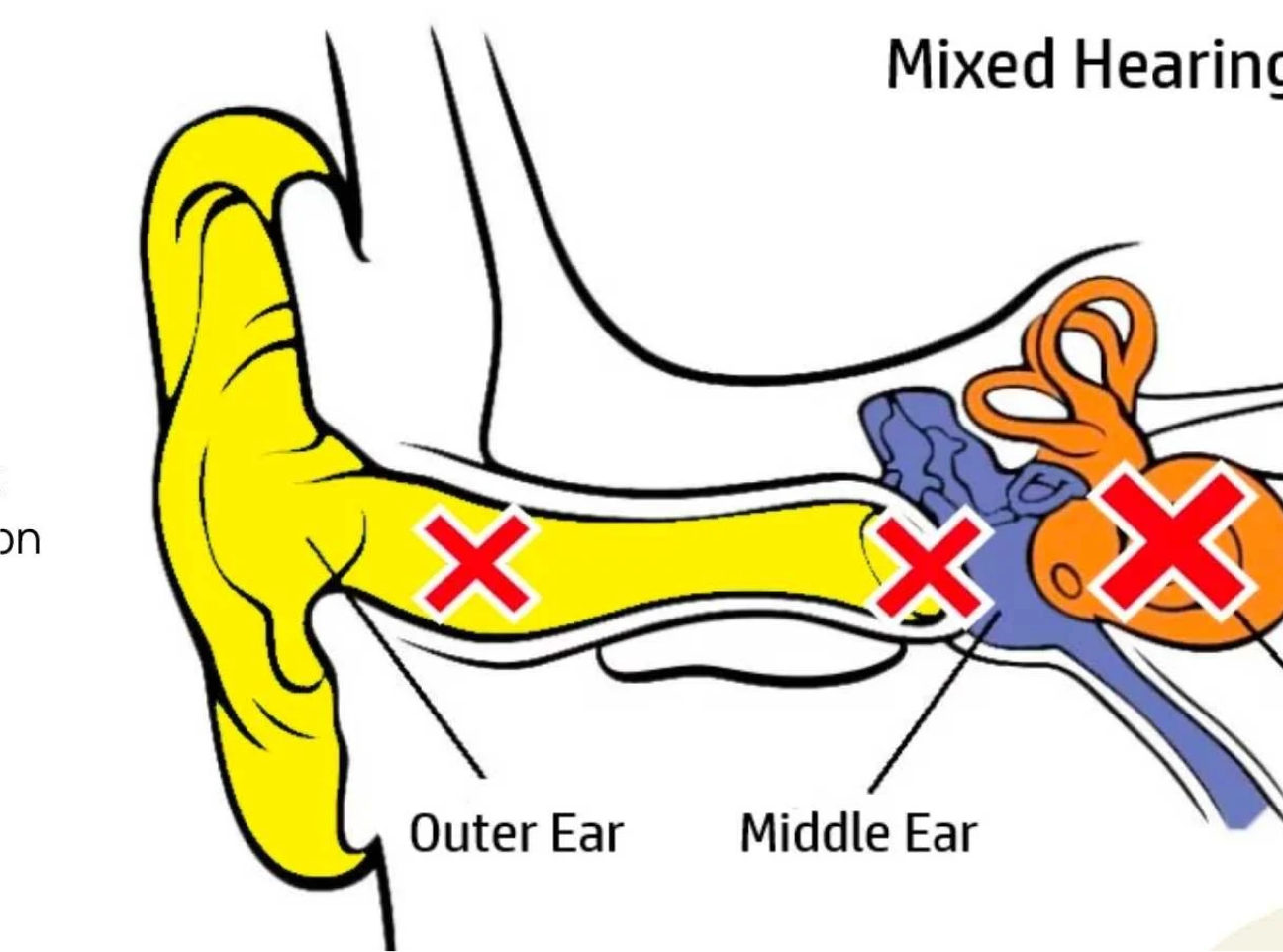
A combination of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.

Challenge:
Solution:

Challenge:
Solution:

Challenge:
Solution:

Challenge:
Solution: