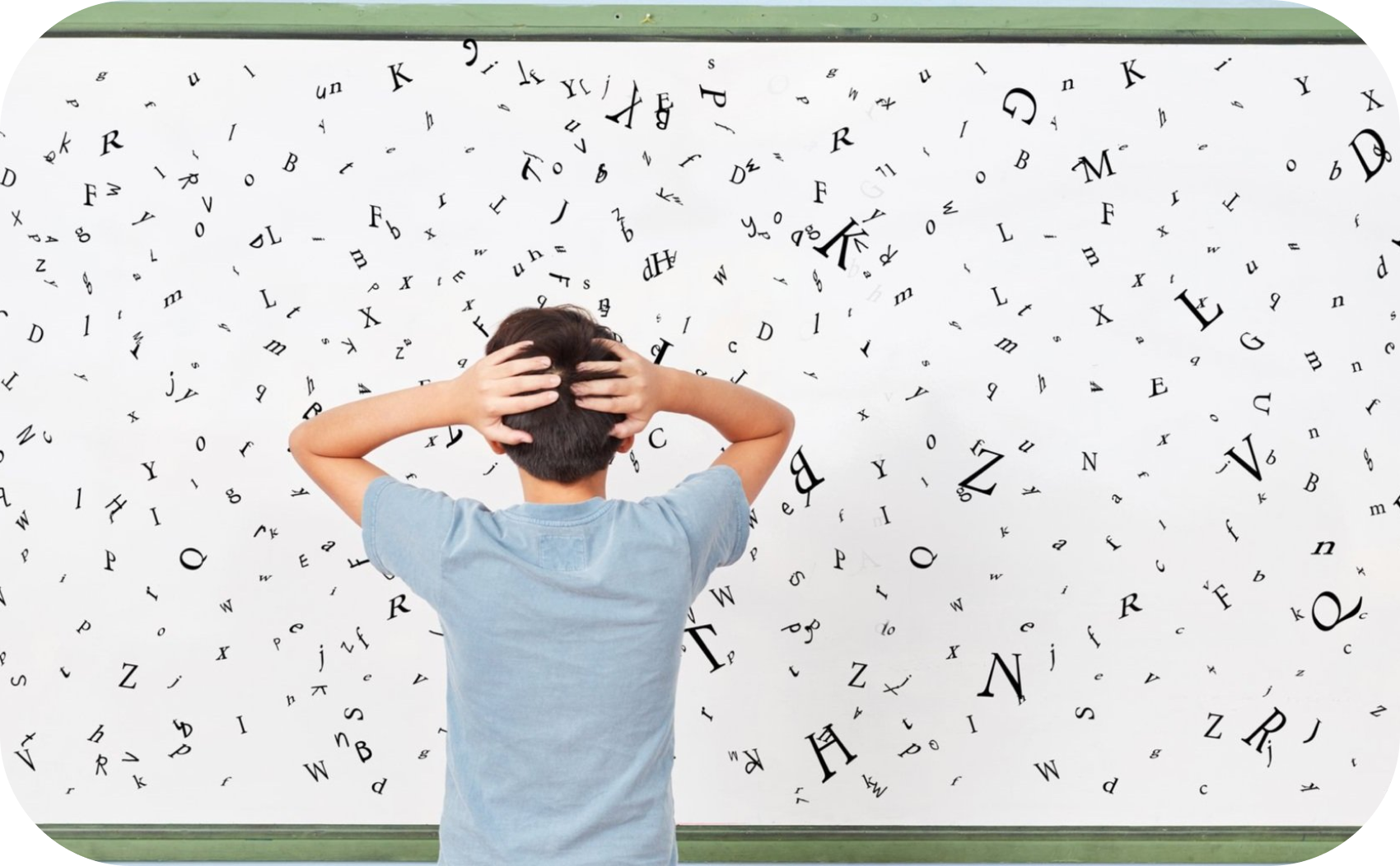
Dyslexia is a common learning difficulty that primarily affects reading, spelling, and writing abilities. People with dyslexia may have trouble recognizing words, decoding text, and processing written language despite having normal intelligence and vision. It’s important to understand that dyslexia is not a reflection of intelligence but rather a neurological condition that requires specific support for learning.

Dyslexia often runs in families, suggesting a genetic link. Children with a family history of dyslexia are at higher risk.
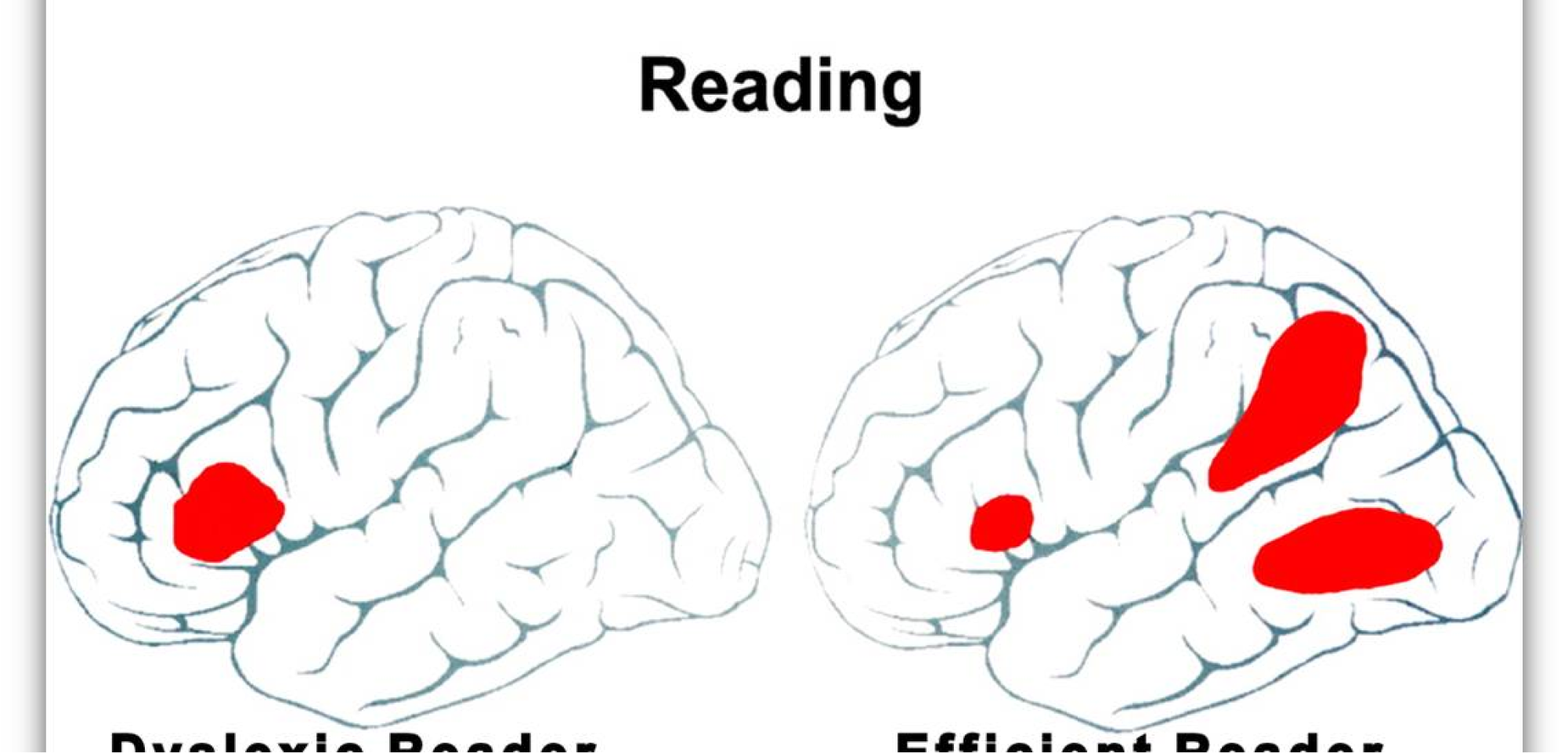
Differences in how certain parts of the brain work together for reading and language processing can contribute to dyslexia.

Babies born prematurely or with low birth weight may have a higher chance of developing learning disabilities like dyslexia.

Limited exposure to language or poor teaching methods may exacerbate the challenges for those with a predisposition to dyslexia.
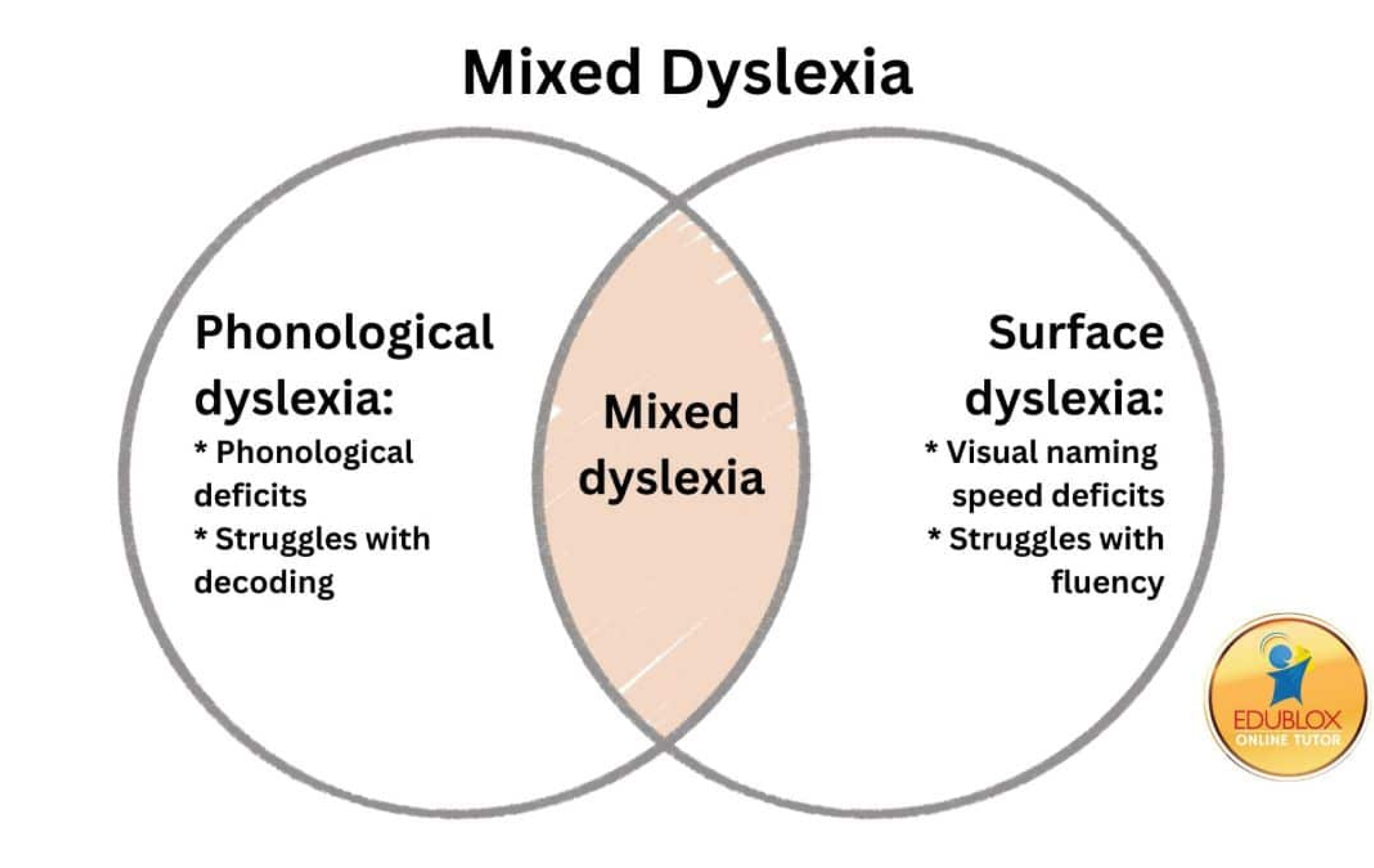

A difficulty with recognizing and manipulating sounds in speech, which impacts the ability to decode words.

A difficulty in recognizing words by sight, leading to problems with spelling and word retrieval.

A challenge with quickly recalling names of familiar objects or colors, affecting reading fluency.

A combination of phonological and rapid naming issues, resulting in more severe challenges in reading and writing.

Challenge:
Solution:

Challenge:
Solution:

Challenge:
Solution:

Challenge:
Solution: